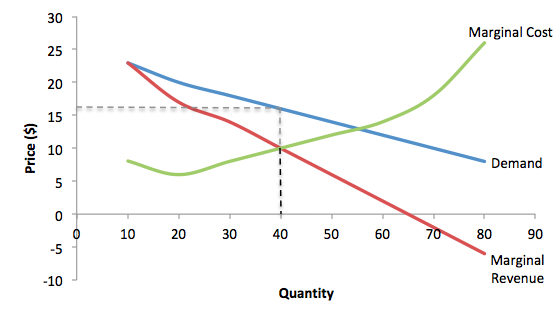
Average Revenue Equals Demand

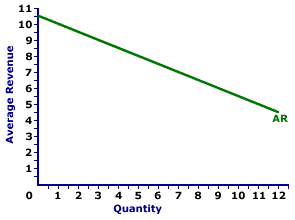
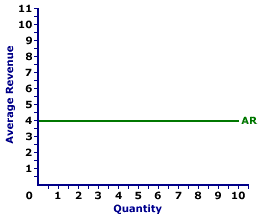
In the special case of a perfectly competitive market a producer faces a perfectly elastic demand curve and therefore doesn t have to lower its price to sell more output.
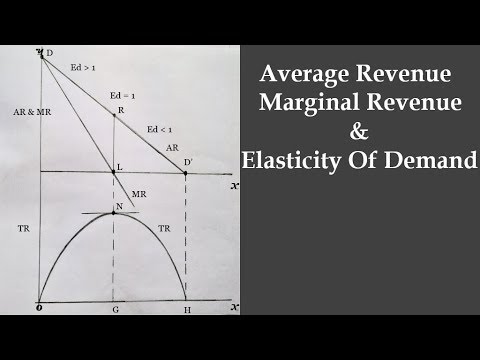
Average revenue equals demand. Ar can be derived from the formula total revenue tr quantity. The elasticity of demand average revenue and marginal revenue has a close relationship. Before you understand the different market forms it is important to know the concepts of total revenue average revenue and marginal revenue. Average revenue and marginal revenue then it can easily find out the third element i e.
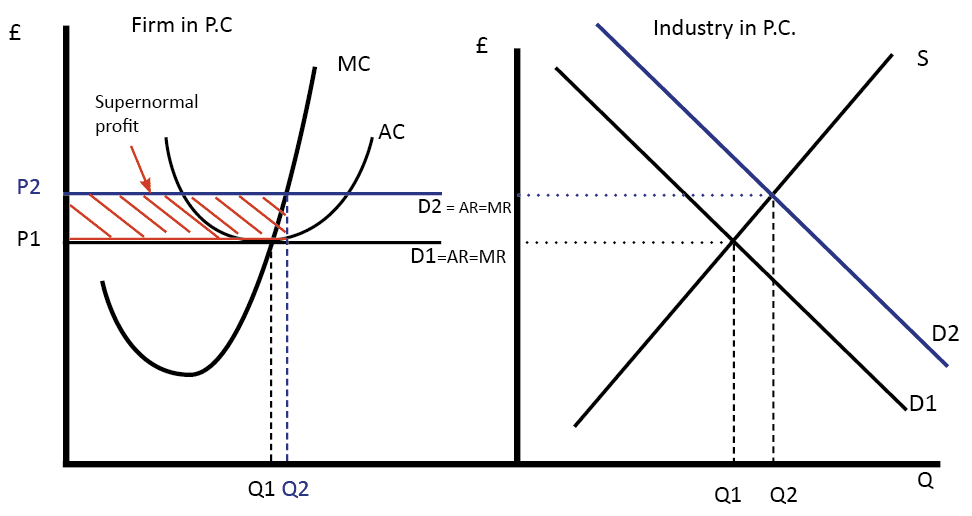
The demand curve represents the different quantities of a good or service. The average revenue and the demand curve. 150 is received from selling 15 units of the product the average revenue will be equal to rs. Average revenue ar is equals to marginal revenue mr inperfect competition pc not imperfect competition.
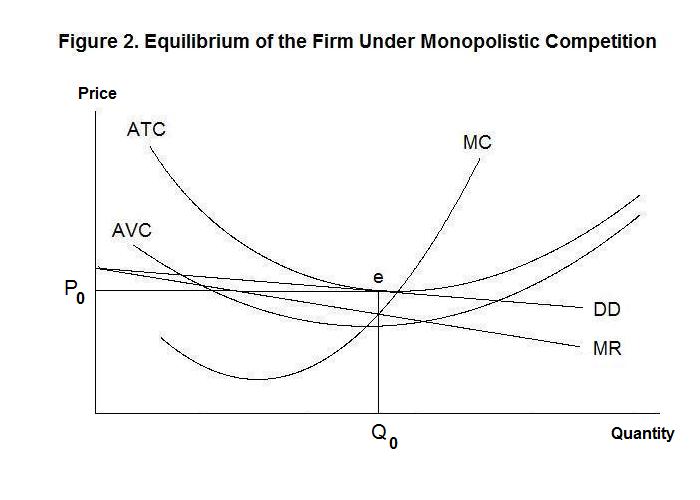
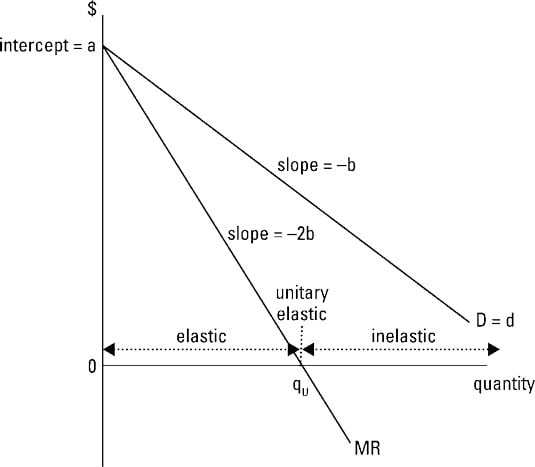
It means when price seems constant marginal revenue is equal to price or average revenue as no loss is incurred on previous units in this case. Figure 2 shows the horizontal demand curve facing a producer is noted as mr also. In our above example when total revenue q equal to rs. Thus when demand elasticity on a firm s average revenue curve is 2 the marginal revenue will be positive and will equal half the average revenue.
Total revenue tr equals quantity of output multiplied by price per unit. 10 per unit the total revenue of the organization would be rs. By applying the above formula it can be shown that at a point on the average revenue curve where elasticity of demand is greater than one marginal revenue will be positive though less than the average revenue. In this article we will clarify these concepts with the help of some examples and look at the behavioral principles.
Since tr price x. The average revenue is the revenue that a firm earns per unit of output sold. The formula for the calculation is. If a firm knows any two of the three elements viz.