Average Revenue Equals Price Times Quantity
Thus average revenue means price.
Average revenue equals price times quantity. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price and average revenue equals the market price. The firm can set its own price based on its output decision. Table 1 summarizes. Average revenue equals price times quantity.
Therefore the total revenue is. Where ar average revenue tr total revenue and q quantity sold. Try to understand the meaning of ar ac. Whereas in your case.
Because total revenue equals price p times quantity q dividing by quantity leaves us with price. Therefore for all types of firms average revenue equals the price of the good. The average and marginal revenue curves are given by the same horizontal line. If ac ar first of all its the case for competitive firm.
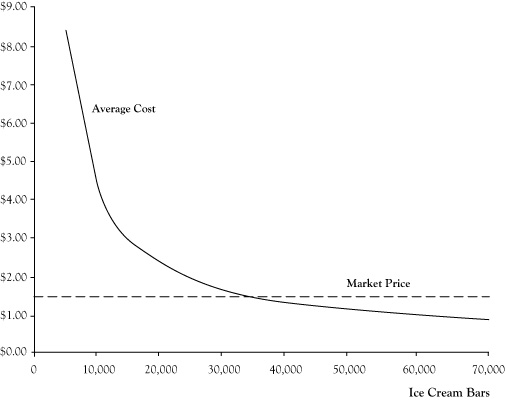
Total revenue is the price times the quantity p q and average revenue is total revenue p q divided by the quantity q. Tr price p total output q for instance if an organization sells 1000 units of a product at price of rs. If the price the firm receives causes it to produce at a quantity where price equals average cost which occurs at the minimum point of the ac curve then the firm earns zero profits. Mathematically ar tr q.
Average revenue deals with revenue profit while average cost the the basic average cost of producing the good. C question 6 of 10 if a firm possesses monopoly power it means that. 20 and the quantity demanded is 15 units. Therefore the total revenue is.
Scenario 2 price is rs. 10 per unit the total revenue of the organization would be rs. Finally if the price the firm receives leads it to produce at a quantity where the price is less than average cost the firm will earn losses. Average revenue is the revenue per unit of the commodity sold.
It is obtained by dividing the total revenue by the number of units sold. Total revenue tr equals quantity of output multiplied by price per unit. Scenario 1 price is rs. 18 and the quantity demanded is 16 units.
The firm is necessarily a monopoly. Tr 1 price x quantity 20 x 15 rs. Tr 2 price x quantity 18 x 16 rs.