Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost Perfect Competition
Marginal revenue equals marginal costs.
Marginal revenue equals marginal cost perfect competition. Marginal revenue and marginal cost figure 7 5. It means when price seems constant marginal revenue is equal to price or average revenue as no loss is incurred on previous units in this case. A perfectly competitive firm should continue to expand output until a. Since we are increasing in increments of 10 we must divide the change in total revenue and total cost by 10.
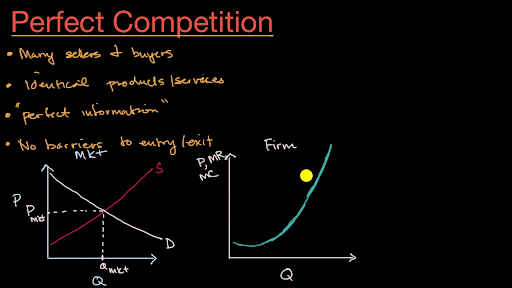
Is equal to its average revenue. Goes below break poittotal revenue will off set total costs. The marginal revenue received by a firm in a perfectly competitive market. A firm under perfect competition faces an infinitely elastic demand curve or we can say for an individual firm the price of the commodity is given in the market.
As mentioned before a firm in perfect competition faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its product that is the firm s demand curve is a horizontal line drawn at the market price level. If for a perfectly competitive firm price exceeds the marginal cost of production the firm should. In economic terms this practical approach to maximizing profits means examining how changes in production affect marginal revenue and marginal cost. As mentioned before a firm in perfect competition faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its product that is the firm s.
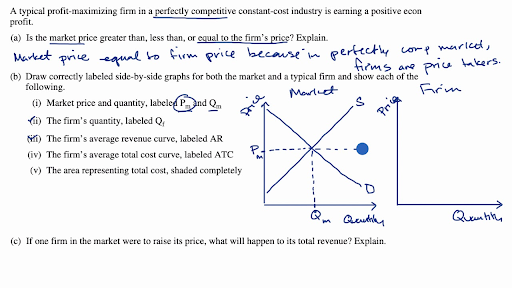
Equilibrium of the firm under perfect competition or marginal revenue marginal cost mr mc rule. Market demand and supply in a perfectly competitive market. A producer under perfect competition can sell additional units the product without reducing price his total revenue increases by the same amount as price. As a reminder for the following table.
The marginal revenue curve shows the additional revenue gained from selling one more unit. Above the break even point the firm will operate at profit earned on each unit of output sold will exceed the average cost of producing a unit of output and total revenue exceed total cost. 14 chapter 8 the firm and the industry under perfect competition 97. The marginal revenue for ex.
Average revenue is greater than marginal revenue. Marginal revenue equals the change in total revenue from selling one more unit. Average revenue equals variable costs. The firm while making changes in the amounts of variable factor evaluates the extra cost incurred on.
Marginal revenue and marginal cost is a per unit value. Total revenue exceeds total costs. Total revenue exceeds variable costs. Equals the market price in perfect competition.