Marginal Revenue Meaning In Accounting

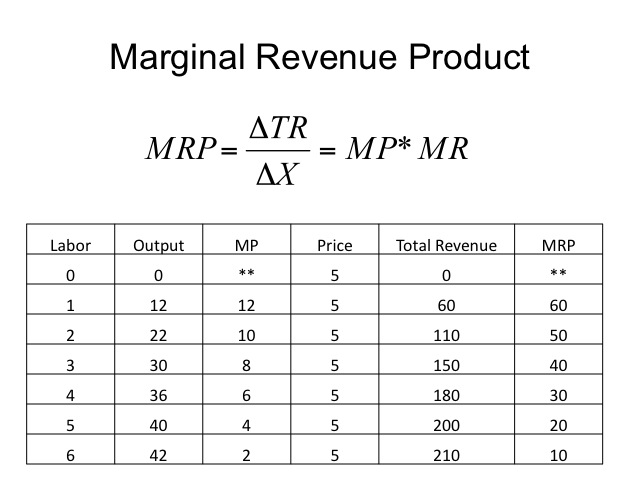
Marginal revenue or marginal benefit is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product sales by 1 unit.
Marginal revenue meaning in accounting. I make 100 000 pens earning a profit of 200 000. A customer wants to buy 10 000 additional pens. In accounting the terms sales and revenue can be and often are used interchangeably to mean the same thing. It can be more easily defined as the variation of the revenue figure after one more unit is sold.
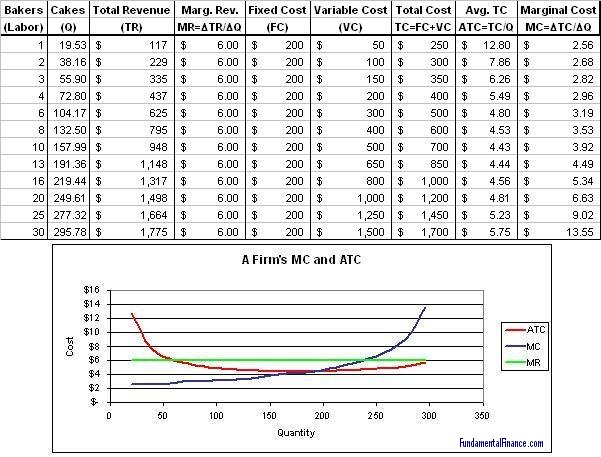
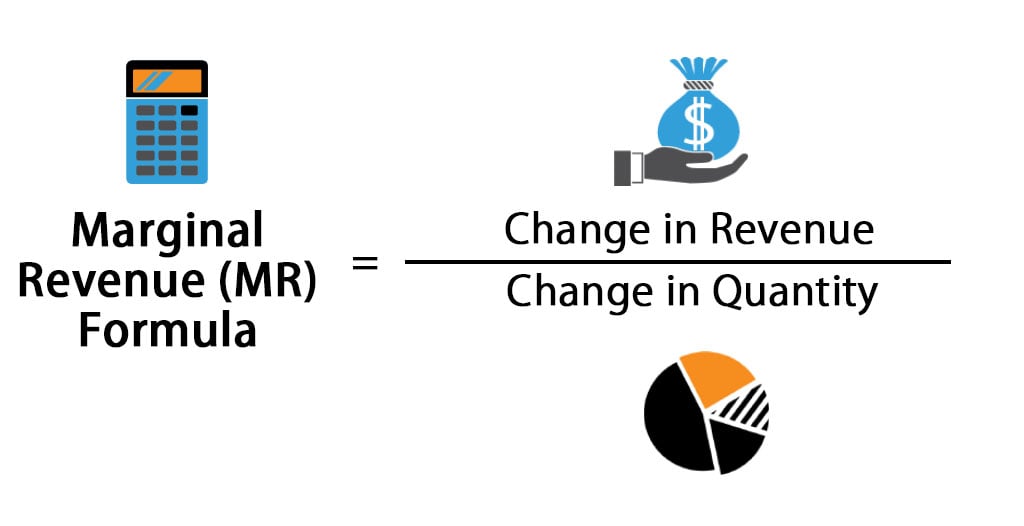
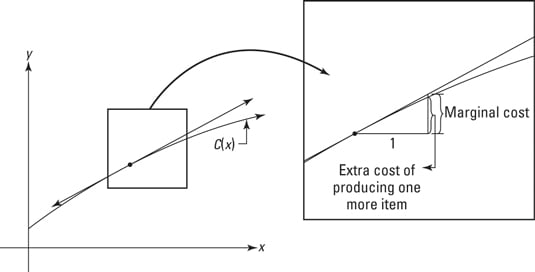
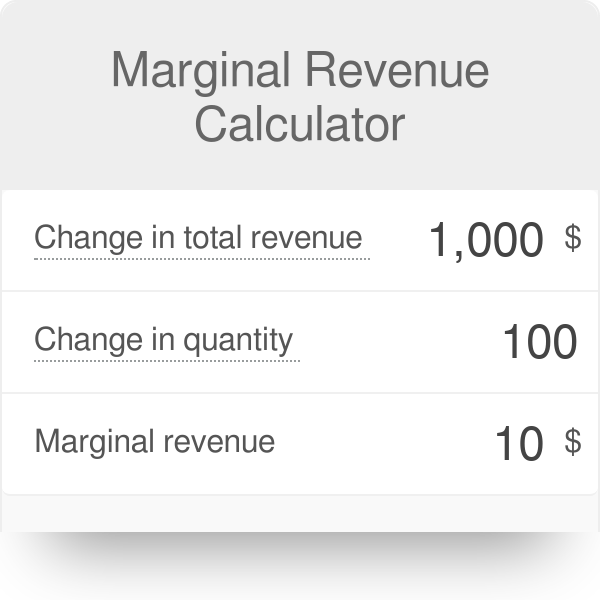
The marginal revenue is 20 000 the difference between 220 000 and 200 000. To derive the value of marginal revenue it is required to examine the difference between the aggregate benefits a firm received from the quantity of a good and service produced last period and the current period with one. The difference in revenue earned by increasing production. It is a financial ratio that is used to compute the overall change in income obtained from the sales of one additional product or unit.
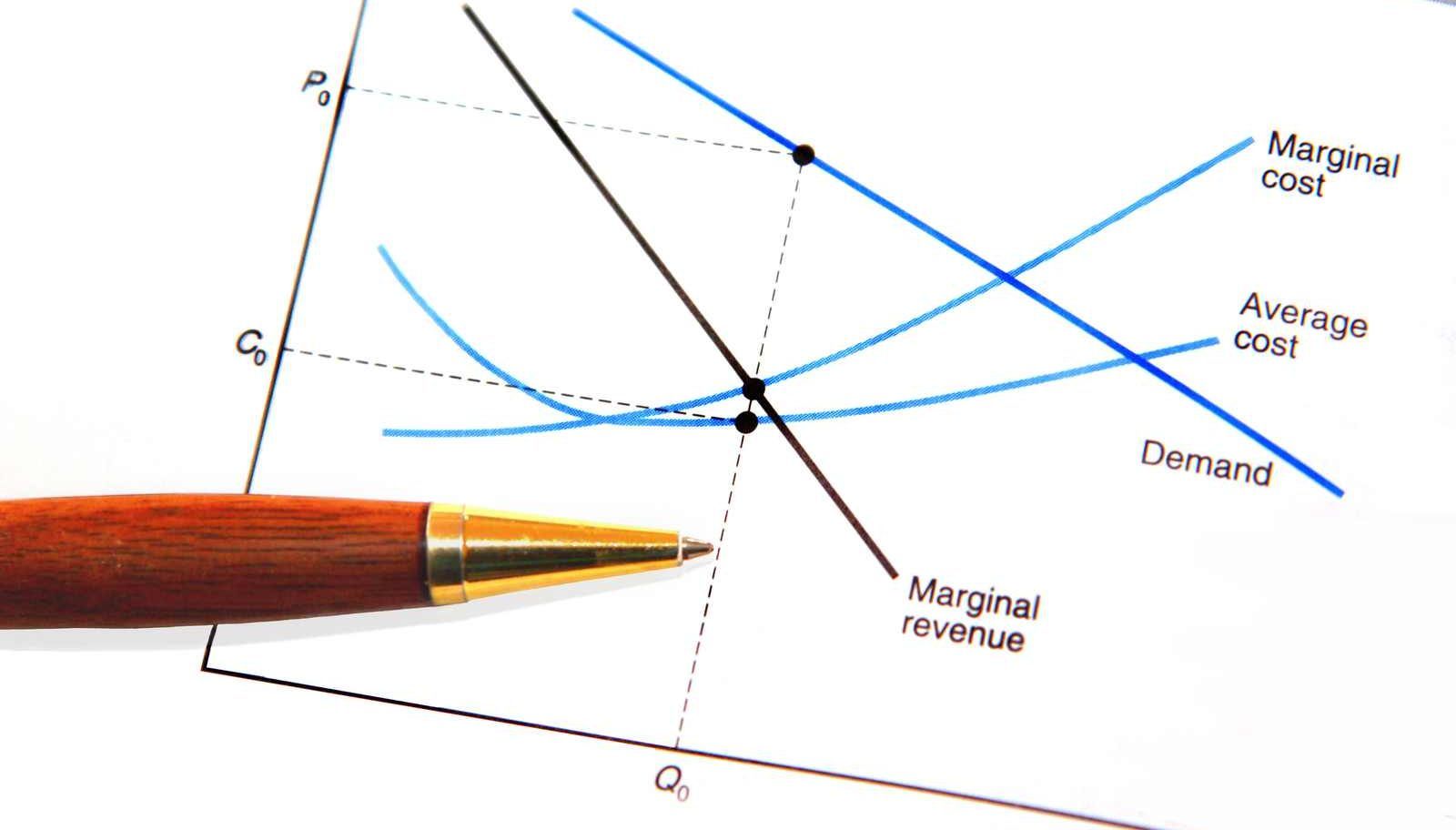
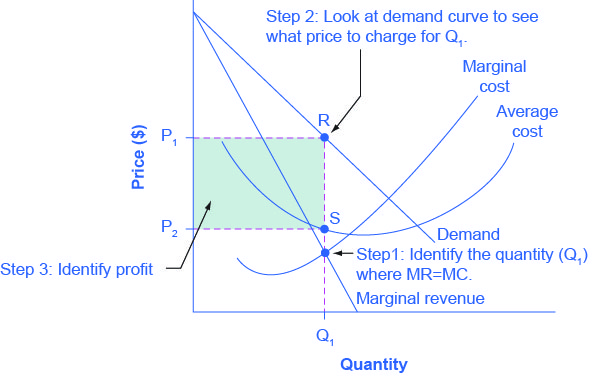
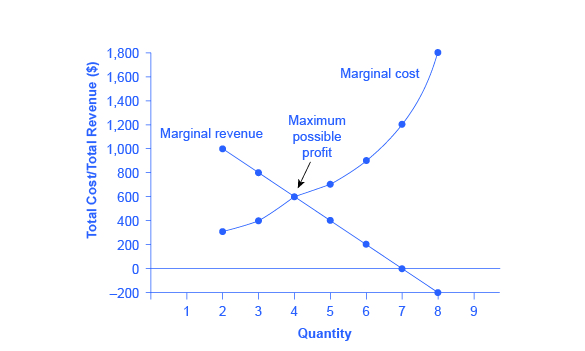
Marginal revenue of a monopolist in case of a monopolist the marginal revenue is not necessarily equal to the price because he faces a downward sloping demand function which results in a downward facing marginal revenue curve. Marginal revenue is the revenue sales revenue sales revenue is the income received by a company from its sales of goods or the provision of services. Harold averkamp cpa mba has worked as a university accounting instructor accountant and consultant for more than 25 years. It shows that the marginal revenue of a perfectly competitive firm is constant and its marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line.
The revenue from the next unit. Marginal revenue mr is the incremental gain produced by selling an additional unit. If i accept that order i will earn 220 000. Marginal revenue is an economic metric defined as the increase in a company s gross revenue from selling one additional unit of its product.
Marginal revenue refers to the increase in revenue realized from the sale of an additional one unit of output. Certificate payroll accounting.







/GettyImages-1186614184-728d67cc52bf408b98967dca574655a0.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/business-people-discussing-in-office-940682222-9829e84f9ad24f84b67a12c3f2f47e19.jpg)