Revenue Cycle Definition Economics

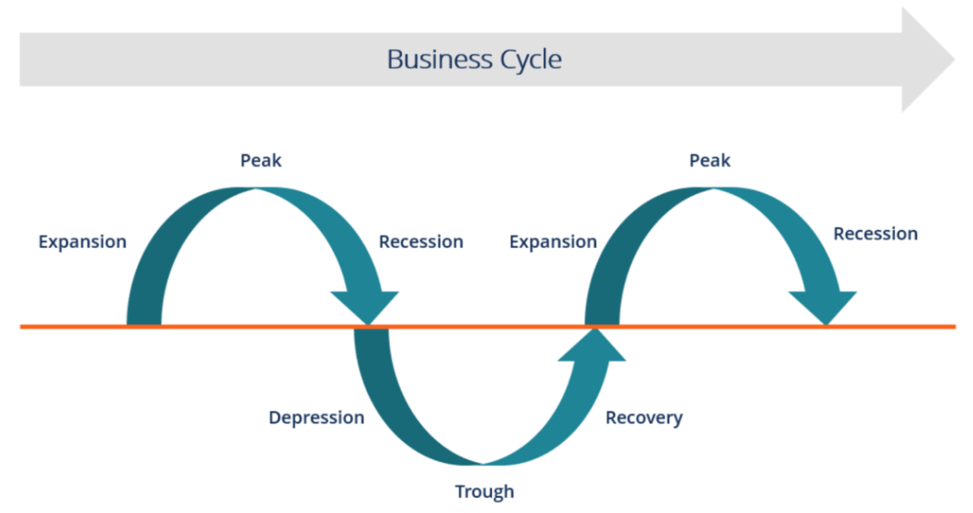
The economic cycle is the natural fluctuation of the economy between periods of expansion growth and contraction recession.
Revenue cycle definition economics. Expansion peak contraction and trough. The table below shows the demand for a product where there is a. Total revenue tr price per unit x quantity. Technically revenue is calculated by multiplying the price p of the good by the quantity produced and sold q in algebraic form revenue r is defined as r p q.
Marginal revenue mr the change in revenue from selling one extra unit of output. The sum of revenues from all products and services that a company produces is called total revenue tr. The average revenue curve shows that the price of the firm s product is the same at each level of output stonier and hague. Revenue in economics the income that a firm receives from the sale of a good or service to its customers.
The objective of the revenue cycle is to provide right product at right price at right place where the customer needs at the right time. Factors such as gross domestic product gdp. Powerful benchmarking tools one of the most effective ways to improve performance and reduce costs is to expand the definition measure ment and interpretation of your organization s revenue cycle beyond receivables cash and a r days. It is obtained by dividing the total revenue by total output.
The revenue cycle begins when the business delivers a product or provides a service and ends when the customer makes the full payment. Revenue cycle performance indicators. Average revenue ar price per unit total revenue output. All businesses and economies go through this cycle though the length varies.
Revenue is the income generated from the sale of goods and services in a market. A survey produced quarterly by the census bureau that provides estimates of total operating revenue and percentage of revenue by customer class for communication key. Revenue cycle performance indicators are. Average revenue refers to the revenue obtained by the seller by selling the per unit commodity.
The federal reserve helps manage the cycle with monetary policy while heads of state and governing bodies use fiscal policy. The ar curve is the same as the demand curve.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)




/UnderstandingTrough2-d597d31e8ba54dd5b4cdc0fbb18b0e3a.png)