Revenue Meaning In Economics
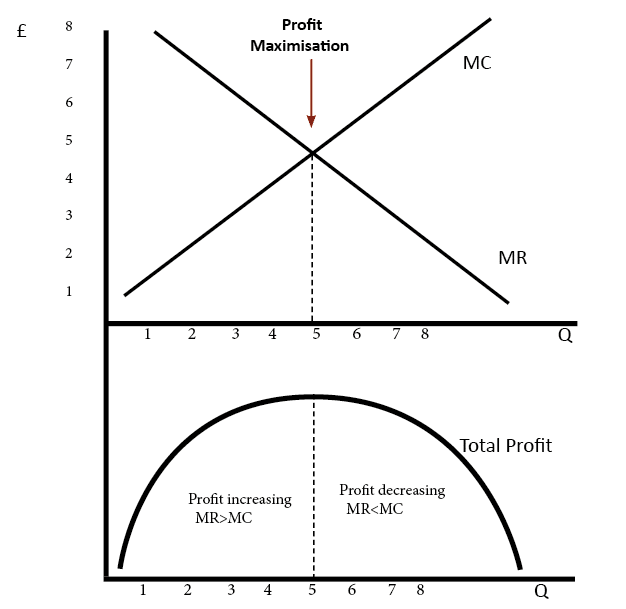
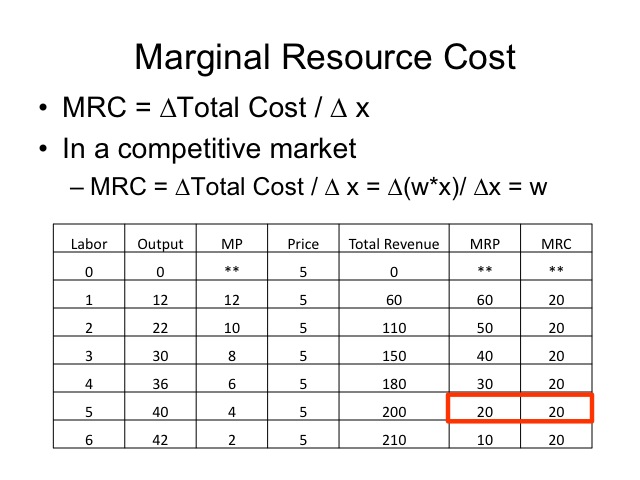
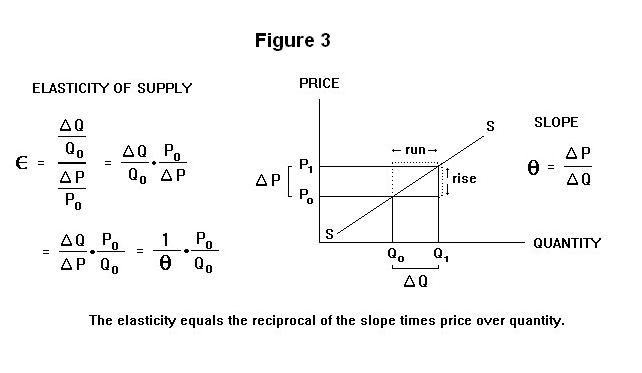
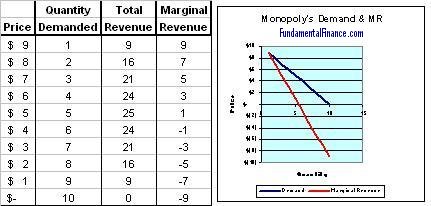
Marginal revenue mr the change in revenue from selling one extra unit of output.
Revenue meaning in economics. Total average and marginal revenue. Supernormal profit is any profit above and beyond the level of normal profit min. 16 000 is known as revenue. Supernormal profit also occurs when average revenue ar is greater than average costs atc.
The ar curve is the same as the demand curve. Read this article to learn about the meaning and concept of revenue micro economics. Supernormal profit occurs when total revenue total cost. The total rent sales or earnings of a company.
Technically revenue is calculated by multiplying the price p of the good by the quantity produced and sold q in algebraic form revenue r is defined as r p q. It is the total income of a business and is calculated by multiplying the quantity of. The revenue concepts are concerned with total revenue average revenue and marginal revenue. The table below shows the demand for a product where there is a.
Total revenue in economics refers to the total receipts from sales of a given quantity of goods or services. The sum of revenues from all products and services that a company produces is called total revenue tr. Revenue in economics the income that a firm receives from the sale of a good or service to its customers. For example if a firm gets rs.
Profit needed to keep firm in business. The amount of money that a producer receives in exchange for the sale proceeds is known as revenue. In the words of dooley the revenue of a firm is its sales receipts or income. The term revenue refers to the income obtained by a firm through the sale of goods at different prices.
16 000 from sale of 100 chairs then the amount of rs. Total revenue tr price per unit x quantity. When negotiating for the purchase of income producing property be sure to inquire about the seller s definition of revenue rather than make the assumption that the seller is using the correct terminology to describe figures supplied to you.



/ExxonIncojmestatement2019June-55cdf08720b24bc7b27ade3de5b6dc32.jpg)