Revenue Reserve Debit Or Credit

For example a business wants to reserve funds for a future building construction project and so credits a building reserve fund for 5 million and debits retained earnings for the same amount.
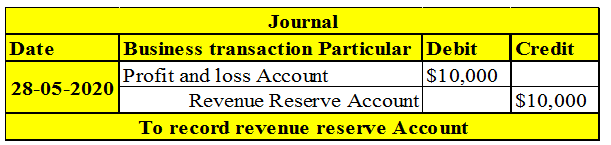
Revenue reserve debit or credit. Revenue profit of the firm are the source of revenue reserves. Revenue reserve is useful for short and mid term urgency requirements. The revenue reserve is the reserve that is created out of the profits of the company generated from its operating activities during a period of time and retained for the purpose of expanding its business or to meet out contingencies in the future. An increase is recorded on the credit side and a decrease is recorded on the debit side of all liability accounts.
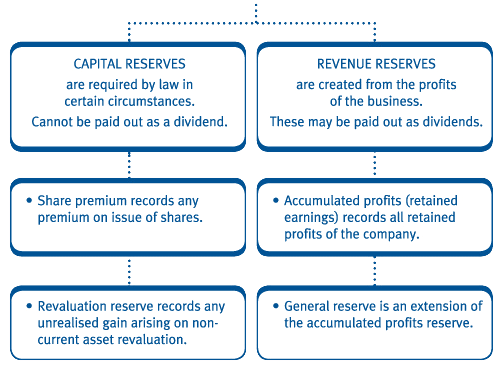
The chart shows the normal balance of the account type and the entry which increases or decreases that balance. The capital reserve is useful for long term purposes. In this case you would debit the reserve account and credit the bonus or dividend account. Revenue reserve capital reserve.
An increase is recorded on the credit side and a decrease is recorded on the debit side of all revenue accounts. Let s illustrate revenue accounts by assuming your company performed a service and was immediately paid the full amount of 50 for the service. Hence contra revenue accounts will have debit balances. For example you would debit the purchase of a new computer by entering the asset gained on the left.
It writes down the value of the inventory with a 10 000 debit to the inventory reserve contra account and a credit to the inventory account. The journal entry is the same as the entry made for bonus issues from the retained earnings. Revenue reserve refers to the sum of money retained in business so as to meet out future contingencies. A company always receive revenue reserve in monetary terms whereas capital reserve is not always in monetary value.
Retained earnings are a popular example of revenue reserve. A debit is an entry made on the left side of an account. This amounts to a 30 000 debit to the cost of goods sold and a 30 000 credit to the inventory reserve contra account. It either increases an asset or expense account or decreases equity liability or revenue accounts.
Another way to decrease or remove the reserve account is to pay dividends to your investors in the form of cash or shares. The company later identifies 10 000 of obsolete inventory. Accounts with balances that are the opposite of the normal balance are called contra accounts. For every credit there must be a debit the debits and credits chart below acts as a quick reference to show you the effects of debits and credits on an account.