Revenue Test Economics Definition

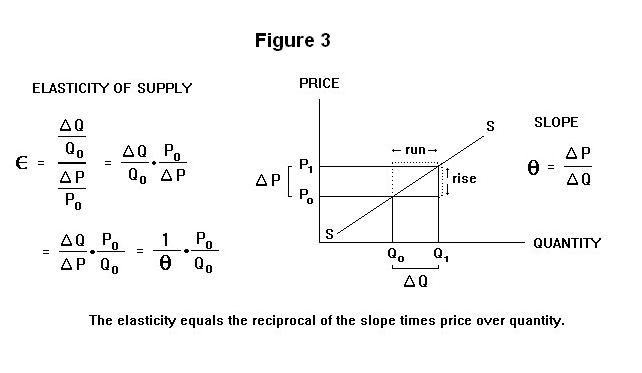
Price elasticity refers to the extent.
Revenue test economics definition. Terms in this set 14 fixed cost. Total revenue tr is found by multiplying price p by output i e. Business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business. Geoff riley frsa has been teaching economics for over thirty years.
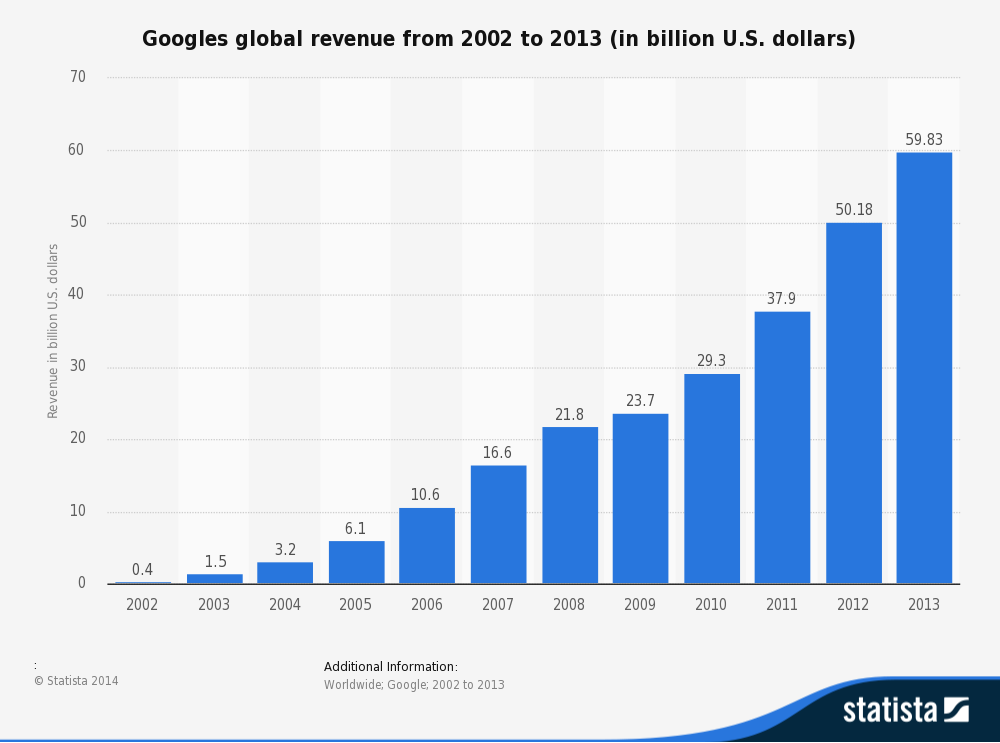
Number of units sold. Total revenue is maximized when marginal revenue zero. In economics the total revenue test is a means for determining whether demand is elastic or inelastic. Revenue in economics the income that a firm receives from the sale of a good or service to its customers.
The sum of revenues from all products and services that a company produces is called total revenue tr. Total revenue test meaning and definition of total revenue test in economics terminology meaning of total revenue test. The table below shows the demand for a product where there is a. If an increase in price causes an increase in total revenue then demand can be said to be inelastic since the increase in price does not have a large impact on quantity demanded if an increase in price causes a decrease in total revenue then demand can be said to be elastic since the.
Technically revenue is calculated by multiplying the price p of the good by the quantity produced and sold q in algebraic form revenue r is defined as r p q. The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students teachers and users of the web their texts will used only for. They tend to be time related such as salaries or rents being paid per month and are. A total revenue test is a way for a company to determine whether demand for its product or good is elastic or inelastic.
Revenue is the income generated from the sale of goods and services in a market. He has over twenty years experience as head of economics at leading schools. A total revenue test approximates the price elasticity of demand by measuring the change in total revenue from a change in the price of a product or service. Cost revenue economics study.
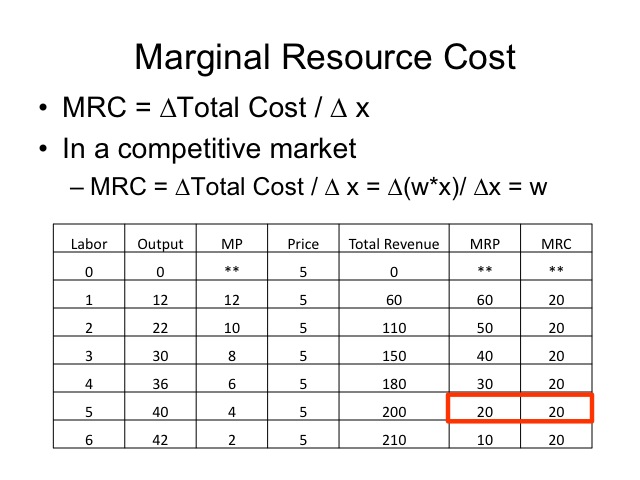
Marginal revenue mr the change in revenue from selling one extra unit of output. The ar curve is the same as the demand curve.