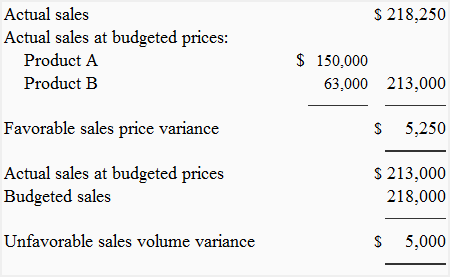Revenue Volume Variance Formula

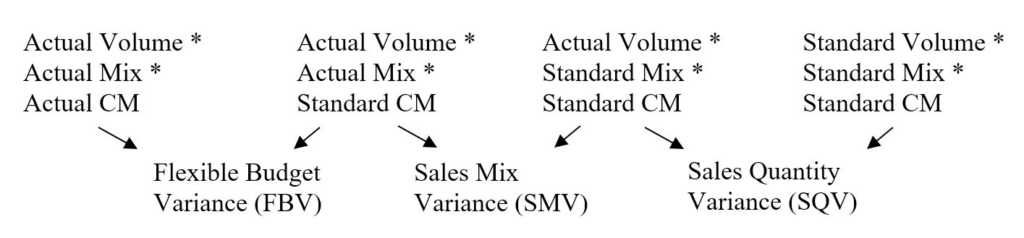
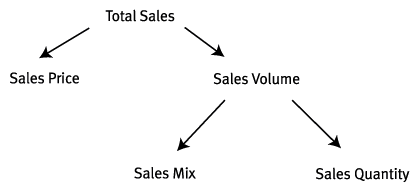
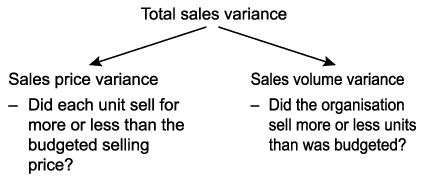
Revenue variance analysis is used to measure differences between actual sales and expected sales based on sales volume days sales in inventory dsi days sales in inventory dsi sometimes known as inventory days or days in inventory is a measurement of the average number of days or time metrics sales mix metrics and contribution margin.
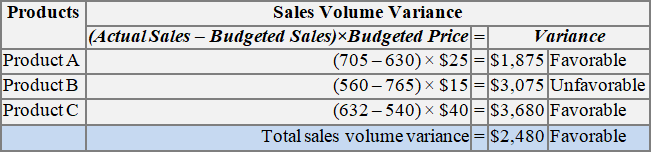
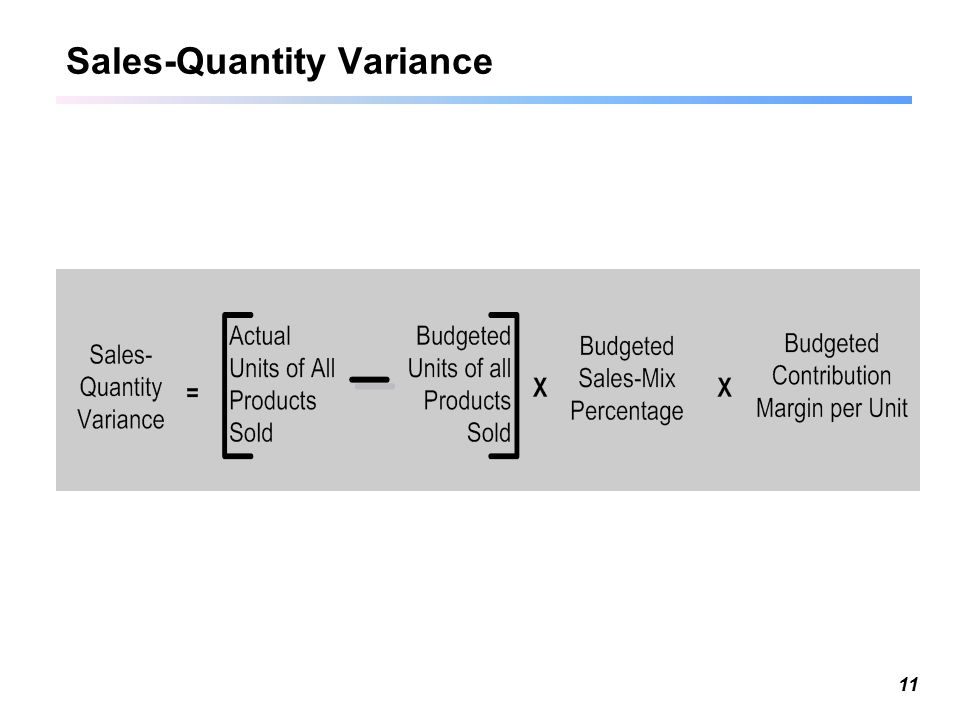
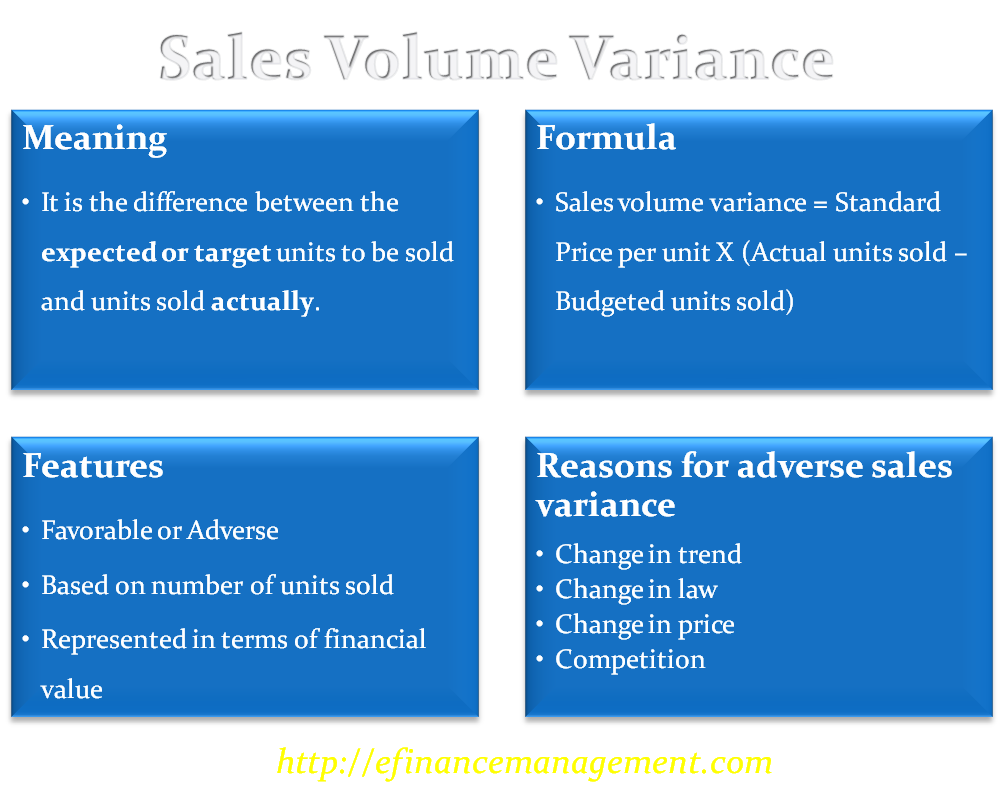
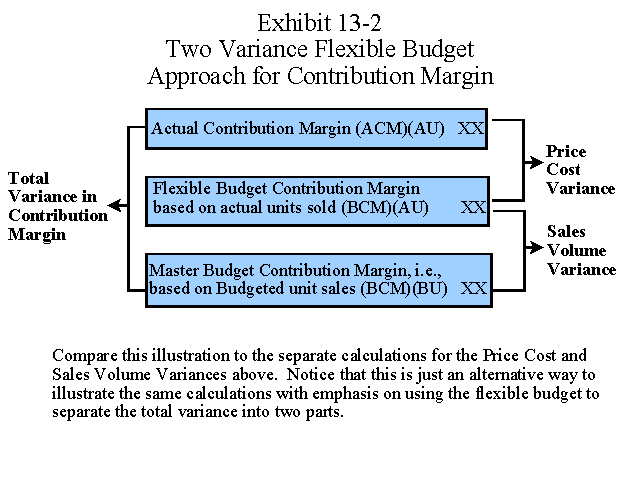
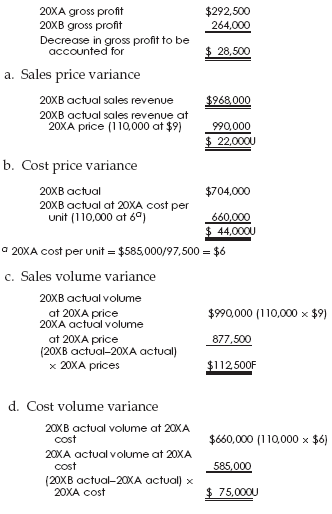
Revenue volume variance formula. A static budget helps businesses stay on track. This information is needed to determine the success of an organization s selling activities and the perceived attractiveness of its products. Revenue variance is the difference between the revenue you budget or expect to earn within a specific period and the revenue your business actually earns within the same period. To calculate sales volume variance subtract the budgeted quantity sold from the actual quantity sold and multiply by the standard selling price.
Revenue variances are used to measure the difference between expected and actual sales. The amount it actually sold. Many businesses use a static budget to create projections of expected revenue and expenses. For example if a company expected to sell 20 widgets at 100 a piece but only sold 15 the variance is 5.