Total Revenue Minus Total Variable Cost Equals

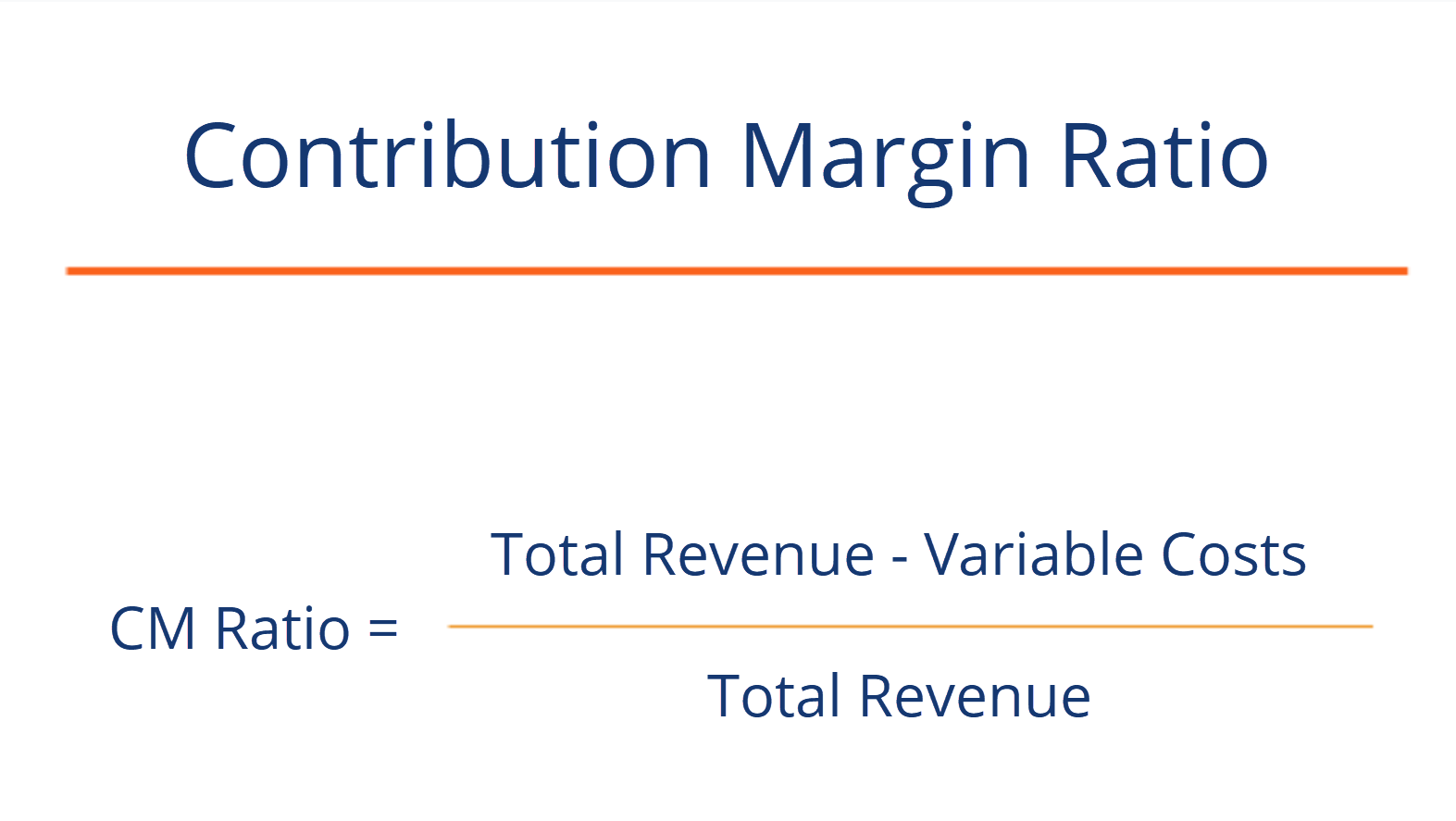
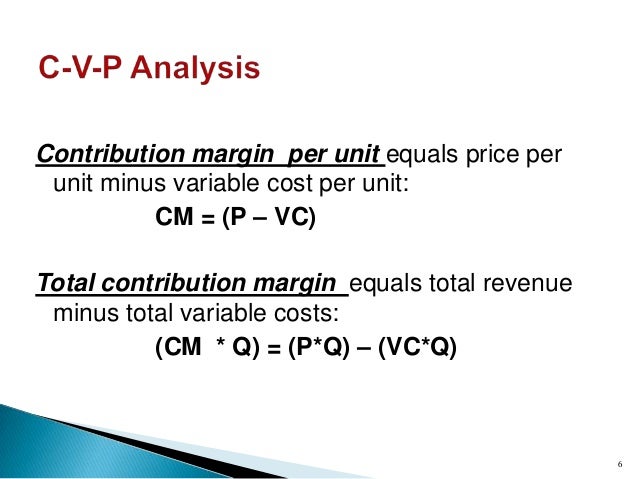
Contribution margin refers to sales revenue minus total variable costs.
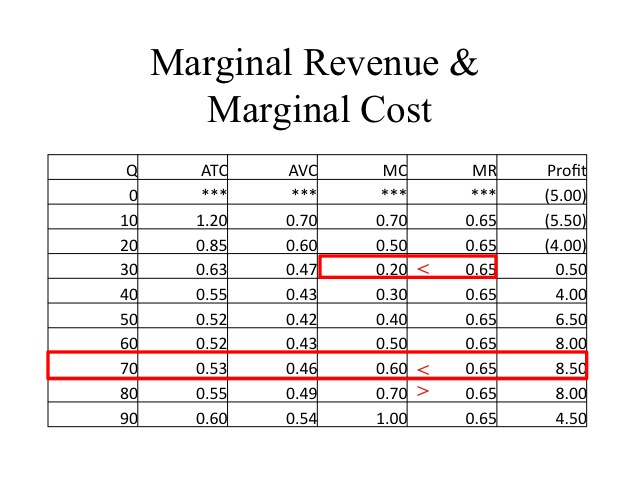
Total revenue minus total variable cost equals. Since we found that producer surplus was 9 in part b profit equals 9 3 or 6. Total revenue minus total costs. Total cost minus total variable cost equals. Total cost divided by the quantity of output tc q.
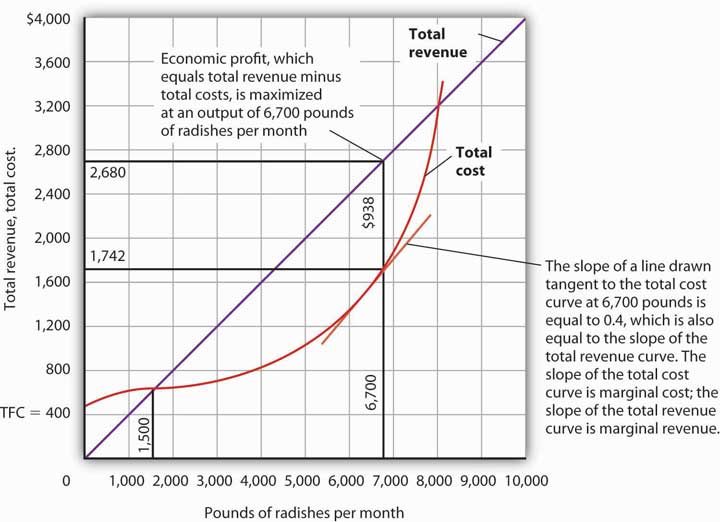
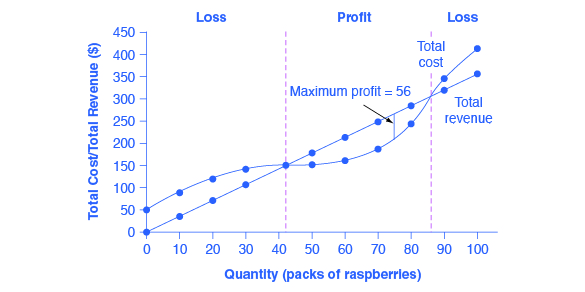
Total profit equals total revenue minus total cost or. This can be increased by increasing the price decreasing the costs while keeping the price constant and or increasing the sales. Tr 9 3 27. Total profit is maximized at the output level where the difference between total revenue and total cost is greatest.
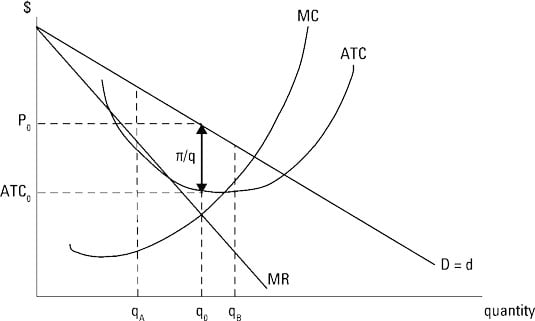
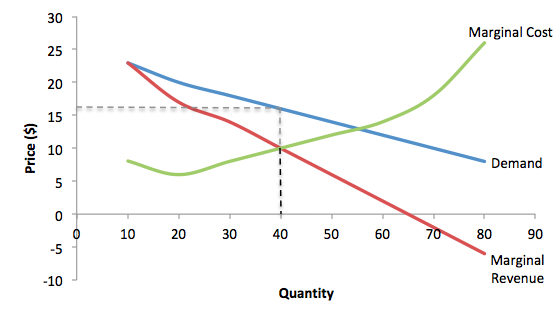
Other things equal marginal cost. For output levels less than or greater than q 0 total profit as represented by the difference between total revenue and total cost is less than the total. Total revenue minus total cost equals profit a production function is significant because it reveals the maximum output that can be obtained from alternative combinations of inputs the sum of fixed cost and variable cost at any rate of output is equal to total cost the distinction between short run and long run supply decisions is based on whether or not there are any fixed inputs a product. Total revenue is price times quantity.
Therefore the total variable cost in producing all the three products will be 880 000 11 48 000 38 85 000 which is equal to 59 13 000. 27 21 6. Total revenue minus total costs is the total profit of a producer. If the market price is below the average variable cost the business is not bringing in enough revenue to compensate for the costs.
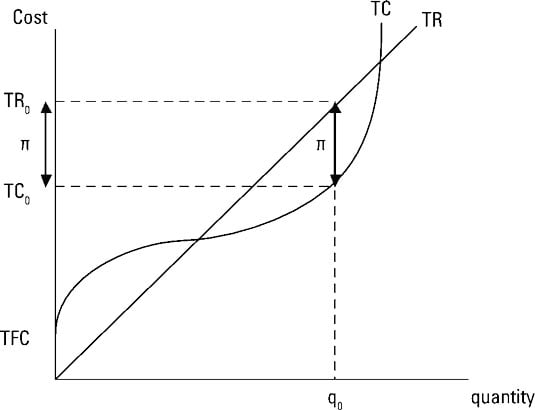
A average fixed costs. Profit is total revenue minus total cost. Fixed cost plus variable cost. The concept of contribution margin is fundamental in cvp analysis and other management accounting topics.
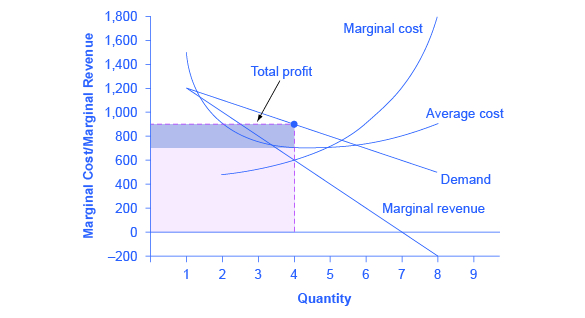
At the output level q 0 total revenue equals tr 0 total cost equals tc 0 and total profit is the difference. Therefore the firm is earning positive economic profits. More easily you might recall that profit equals producer surplus minus fixed cost. It is the amount available to cover fixed costs to be able to generate profits.
In the illustration this occurs at the output level q 0. Vary with the quantity produced. The increase in total cost from producing one more unit. At q 0 your total revenue equals tr 0 and your total cost equals tc 0.
Do not vary with the quantity of output produced. When the total revenue is than the total cost the level of profit that occurs is a loss. Your total profit equals total revenue minus total cost and is represented by the double headed arrow labeled ð. Therefore the calculation of total variable cost will be as follows 222000 00 17 50.