Average Revenue Function Under Perfect Competition

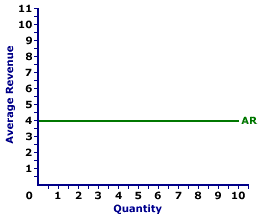
Average and marginal revenue curves under perfect competition.
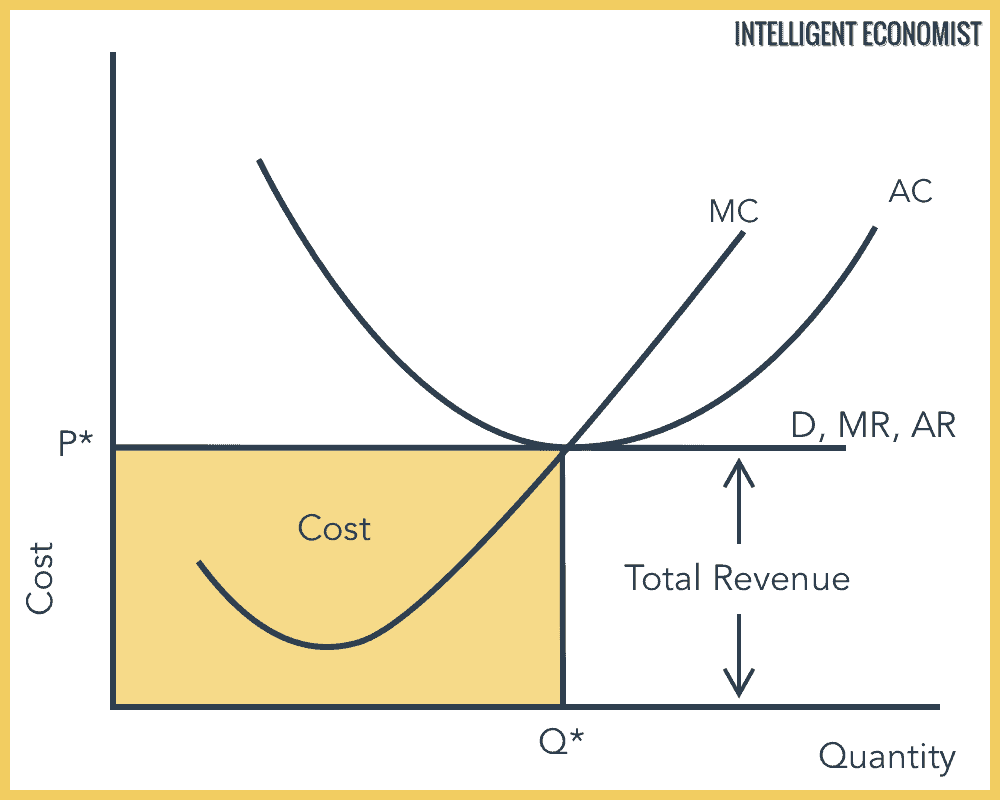
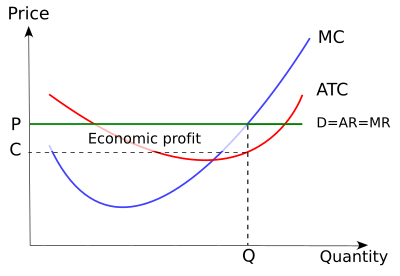
Average revenue function under perfect competition. In all other markets ar curve slopes downwards and mr curve lies below it. In pure monopoly ar curve is a rectangular hyperbola and mr curve coincides with the horizontal axis. The average revenue curve is therefore always equal to marginal revenue and so both the curves ar and mr coincide. These curves show the behaviour of the revenue of a firm.
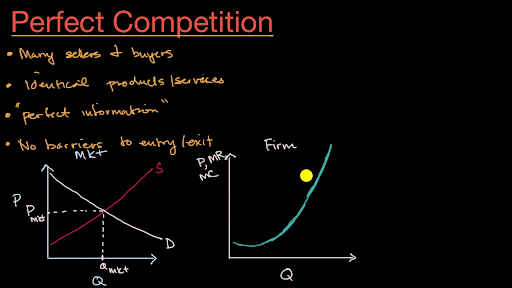
In the light of such conditions the demand curve is perfectly elastic a straight line parallel to the x axis. This means when average revenue or price falls units of out a rises and when average revenue price raises quantity sold falls. We are already aware of the fact that ar curve and demand curve are same. The total revenue of the firm is.
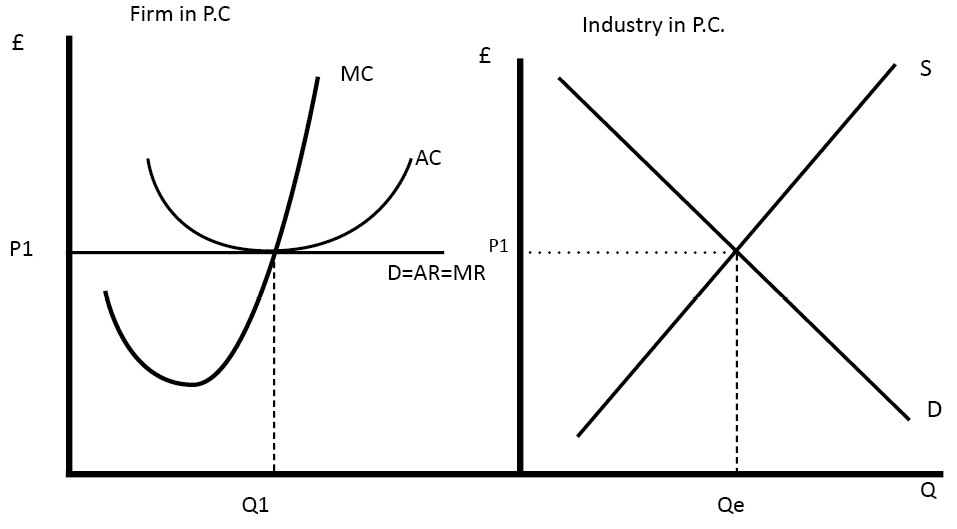
The corresponding ar and mr curve is one and the same and horizontal to the x axis. Let us see how the revenue curve of a firm behaves under perfect competition. The total out put is sold by the seller but bought by the buyers. In prefect competition every firm sells its output at a given price and can sell as much as it likes at this price.
Under perfect competition average revenue curve is a straight horizontal line and is equal to mr. In oligopoly however ar curve cannot be drawn with. Hence the firm s average and marginal revenue become constant and equal. Revenue and perfect competition.
This implies that average revenue curve under imperfect competition falls. Firms are price takers and their average and marginal revenue are the same. Under perfect competition the additional output is sold at the price at which the first unit is sold. For instance when the market prices of a commodity is 5 per unit the firm sells 10 units.
Thus the ar curve is a straight line parallel to. A producer under perfect competition can sell additional units the product without reducing price his total revenue increases by the same amount as price. In perfect competition uniform prices exist which are fixed by the market. The revenue curve of a firm is majorly represented by the average revenue and marginal revenue curves of a firm.
The average revenue curve is thus the something as the demand curve at.