Marginal Revenue Equals Average Revenue

Ideally the firm must continue expanding until the marginal revenue equals the marginal cost.
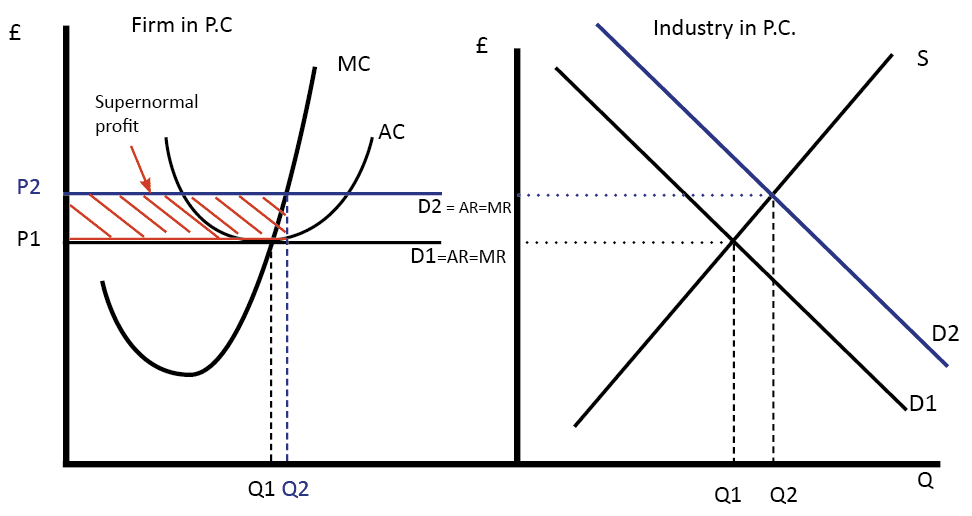
Marginal revenue equals average revenue. Also apart from being equal the marginal cost curve must cut the marginal revenue curve from below explanation. This means that the additional revenue the firm earns for an extra unit sold is equal to 5 which is the same as the average revenue the firm earns for each unit sold. One of them is that no firm can decide or influence the market price of a good by changing its quantity. Therefore in perfect competition average revenue is equal to marginal revenue as a single price the ruling market price is charged for all units sold by firms.
Total revenue increases at a constant rate as additional units are produced and sold. 10 per unit the total revenue of the organization would be rs. Relationship between total average and marginal revenue. There are some basic assumptions to be satisfied in order to consider a market as a perfectly competitive market.
Since price is constant marginal revenue is also constant. Average revenue is the revenue per unit of the commodity sold. Mathematically ar tr q. Total revenue is a function of output which is mathematically expressed as.
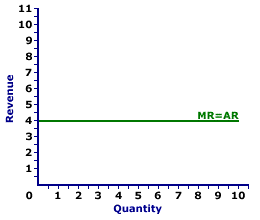
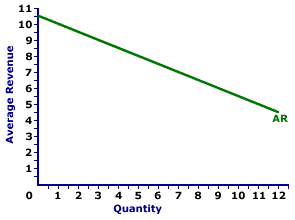
It is obtained by dividing the total revenue by the number of units sold. That is not actually true in all cases perhaps not entirely true in any real case. The case of perfect competition when for an individual firm average revenue or price remains constant and marginal revenue is equal to average revenue is graphically shown in fig. Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue which results from the sale of one more or one.
According to this principle if a unit of production adds more to the revenue than to the cost then the said unit increases the. 21 2 average revenue curve in this case is a horizontal straight line i e parallel to the x axis. Indicated by the same horizontal line. Tr price p total output q for instance if an organization sells 1000 units of a product at price of rs.
Since price is constant marginal revenue equals price or average revenue. The average revenue curve shows that the price of the firm s product is the same at each level of output stonier and hague. In our example average revenue is 500 100 5. Where ar average revenue tr total revenue and q quantity sold.
Total revenue tr equals quantity of output multiplied by price per unit. Imperfect competition output q average revenue price total revenue tr ar x q marginal revenue mr tr n tr n 1 1 10 10 2 9 18 8 3 8 24 6 4 7 28 4 5 6 30 2 6 5 30 0 7 4 28 2 8 3 24 4 9 2 18 6 10 1 10 8 6. Thus average revenue means price. Price ar mr.