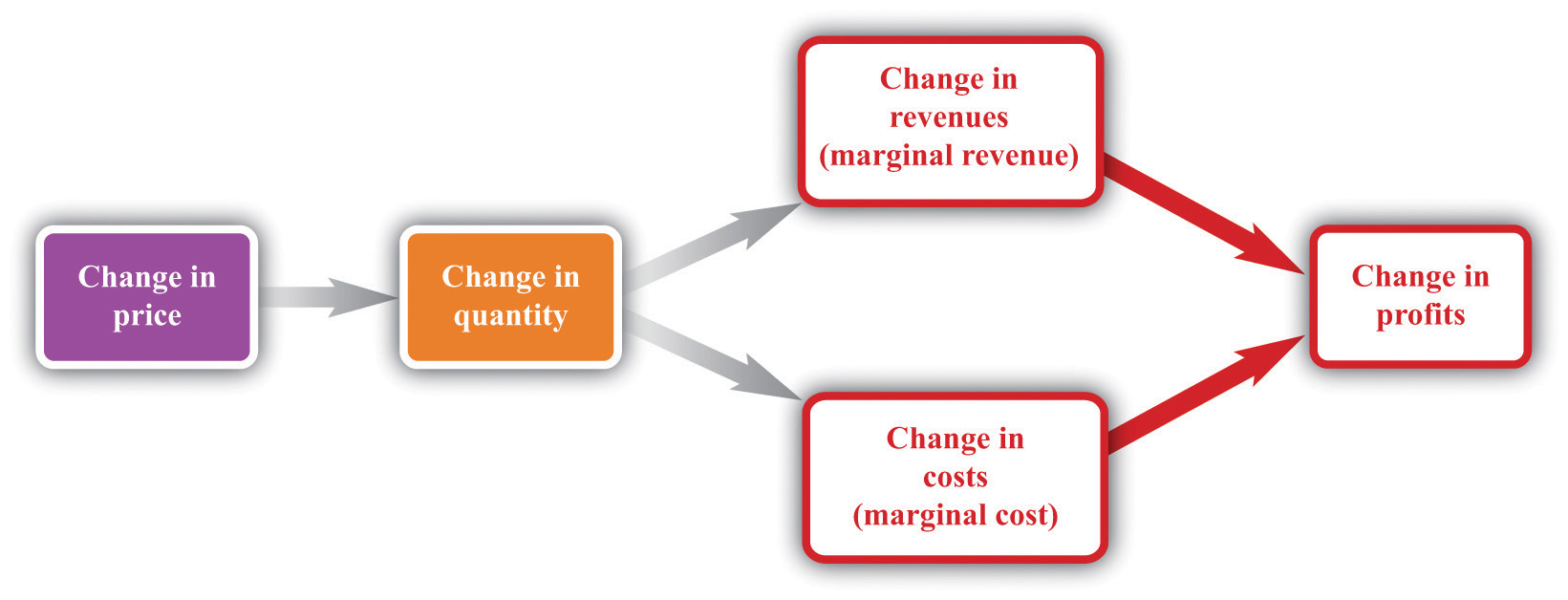
Marginal Revenue Minus Marginal Cost Is Equal To
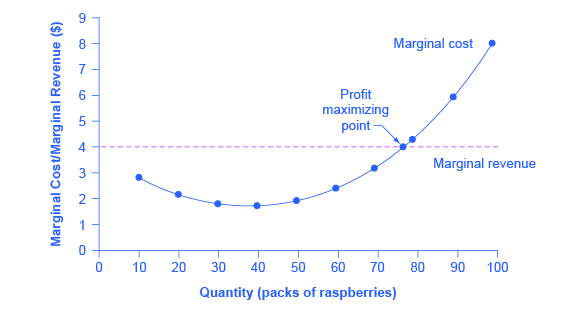
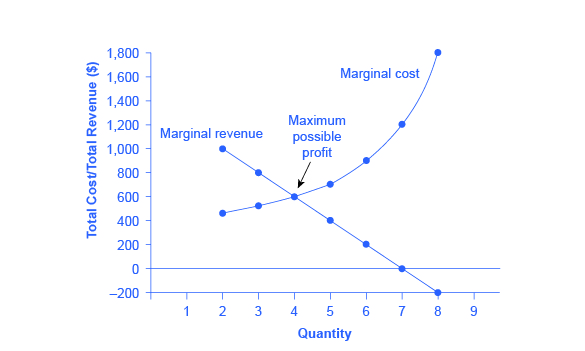
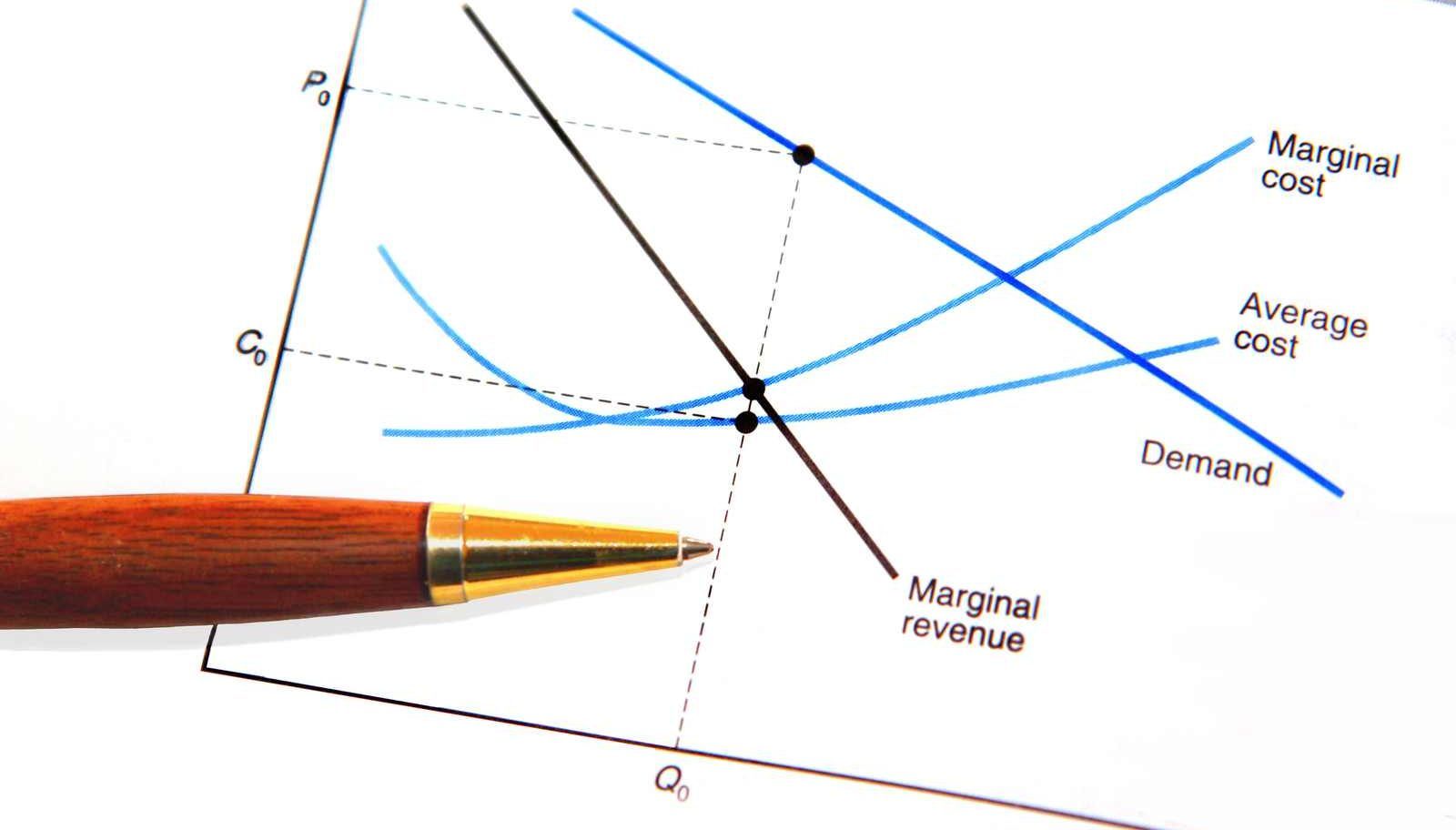
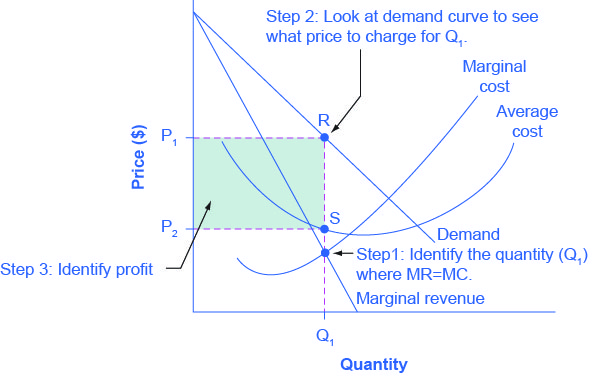
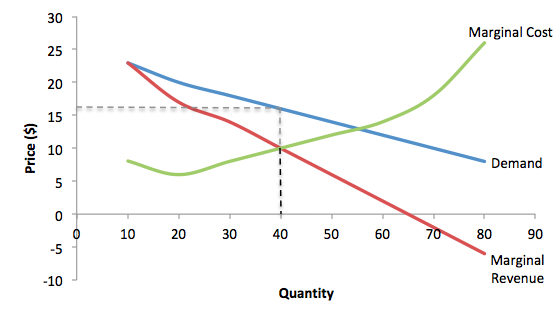
When marginal costs equal marginal revenues a facility is assumed to be operating at its best efficiency which will work to maximize profits.
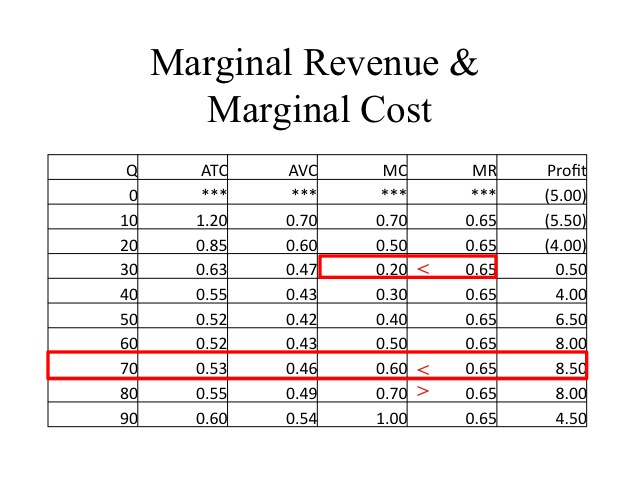
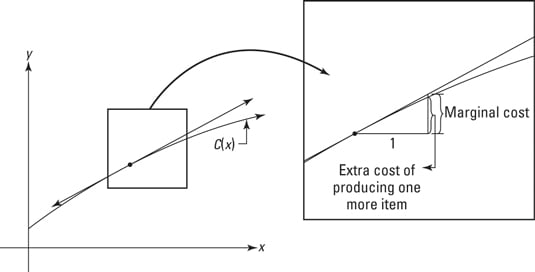
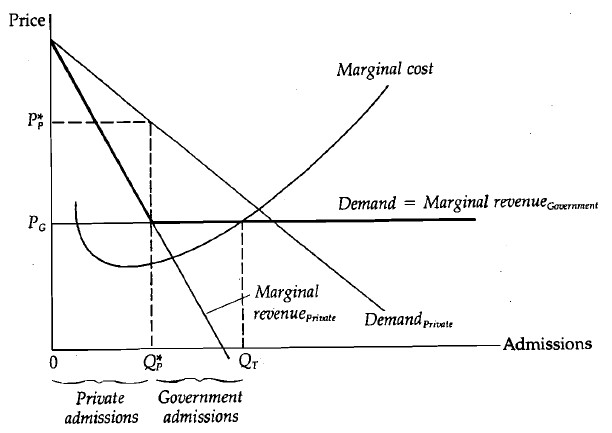
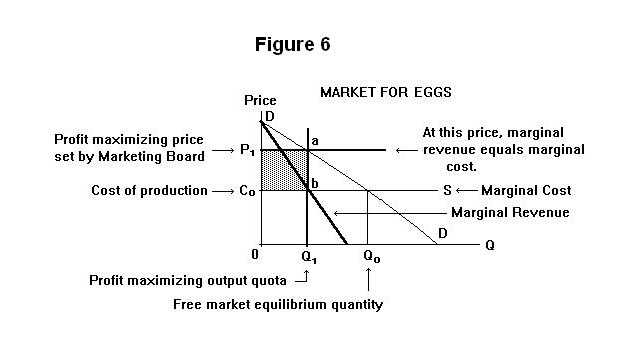
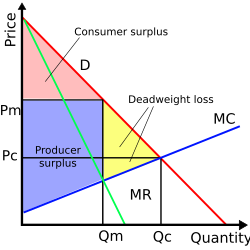
Marginal revenue minus marginal cost is equal to. The relationship between marginal costs and marginal revenues helps to determine production levels. The market determined price for your good is 80. Thus firms should continue producing more output until. Marginal cost is the additional cost a firm must incur when it sells an additional unit of output for example in that same coffee shop if the ingredients for the coffee costed 3 dollars than the.
Therefore your total revenue equals. Economists call the added revenue marginal revenue and the added cost marginal cost. This is a state of best fit for profit and production and price. When marginal revenues equal marginal costs you have achieved your maximum profit level.
Profit equals total revenue minus total cost. The marginal cost of production and marginal revenue are economic measures used to determine the amount of output and the price per unit of a product that will maximize profits. Marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned by selling an additional unit of output for example if you owned a coffee shop which sold coffees for 5 each the marginal revenue would be 5. Given businesses want to maximize profit they should keep producing more output as long as an additional unit adds more to revenue than it adds to cost.