Monopoly Average Revenue Equals Demand
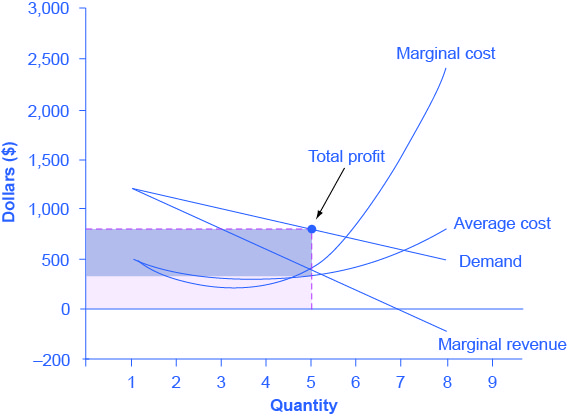
The first two columns show the monopolist s demand schedule.
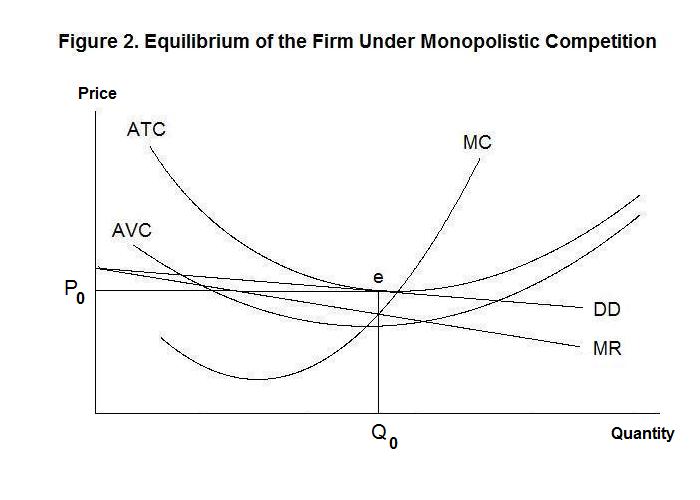
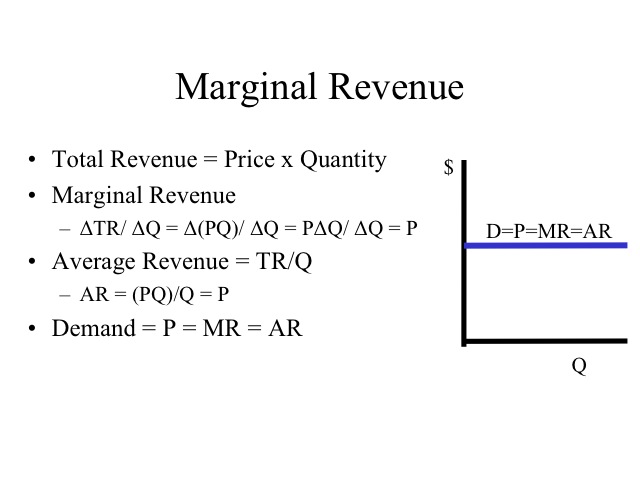
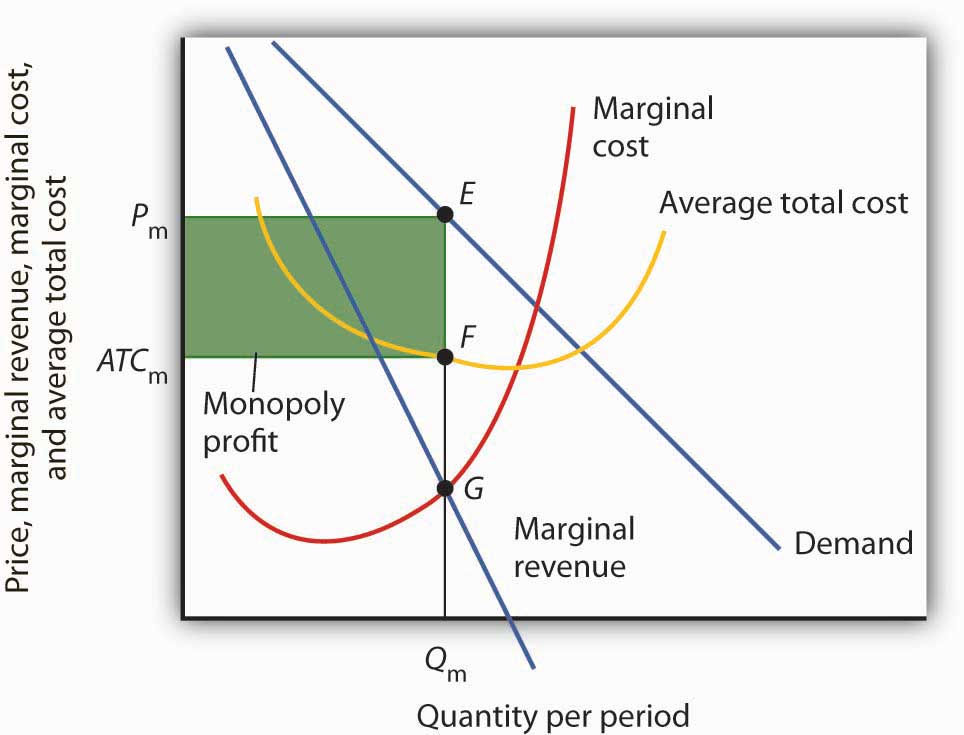
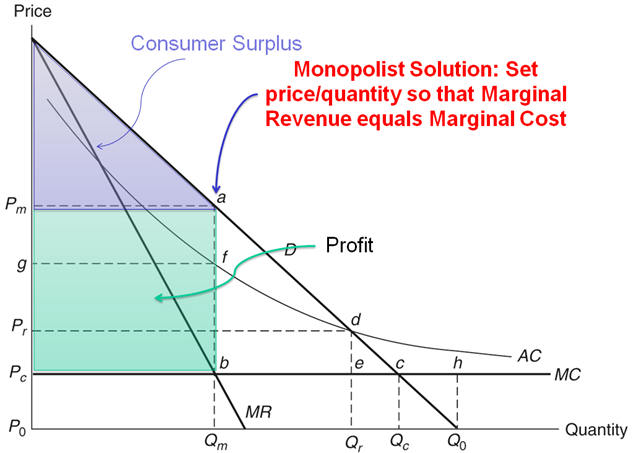
Monopoly average revenue equals demand. Tr x p x x. For a straight line demand curve the marginal revenue curve equals price at the lowest level of output. Table 1 a monopoly s total average and marginal revenue. The relation between marginal revenue and average revenue is explained with the help of a schedule and a diagram.
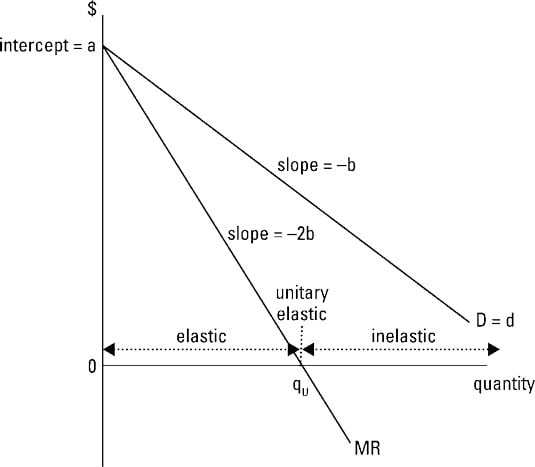
Specifically the steeper the demand curve is the more a producer must lower his price to increase the amount that consumers are willing and able to buy and vice versa. The demand curve is important in understanding marginal revenue because it shows how much a producer has to lower his price to sell one more of an item. Define average revenue as ar x tr x x. Average revenue can be represented in a table or as a curve.
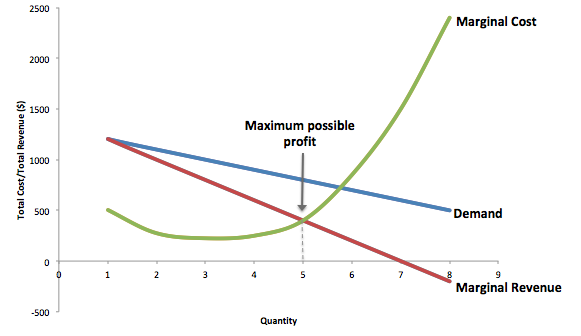
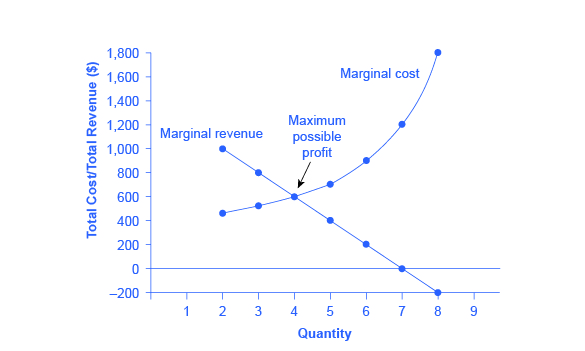
Table 1 shows how the monopoly s revenue might depend on the amount of water produced. Graphically mr and demand have the same vertical axis as output increases marginal revenue decreases twice as fast as demand so that the horizontal intercept of mr is halfway to the horizontal intercept of demand. The relationship between the monopolist s marginal revenue and price i e average revenue is reflected in the price elasticity of the industry demand curve. Since p p 1 we can write equation 1 as.
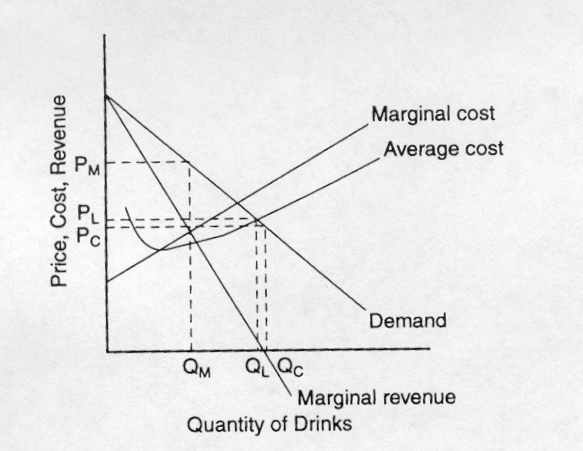
As the monopolist s demand curve is negatively sloped the marginal revenue is here no longer equal to price or average revenue. Make one assumption that the seller uses linear pricing all units sold at the same price. The constant or decreasing nature of average revenue is a prime indication of the market control of a firm. It is true almost by definition.
It is less than the price ar at every level of output except the first. Let p x denote the inverse demand then you get total revenue as a function of quantity chosen by the monopolist to be. Clearly marginal revenue equals zero if the price elasticity equals one. Consider a town with a single producer of water.
Average revenue is nothing but total revenue div. The average revenue curve is also the demand curve facing the firm. The average revenue is also the curve which represents the price of a product. Average revenue curve is often called the demand curve due to its representation of the product s demand in the market.