Revenue Definition As Per Accounting Standard

This is the best notes on accounting standard 9 revenue recognition with examples.
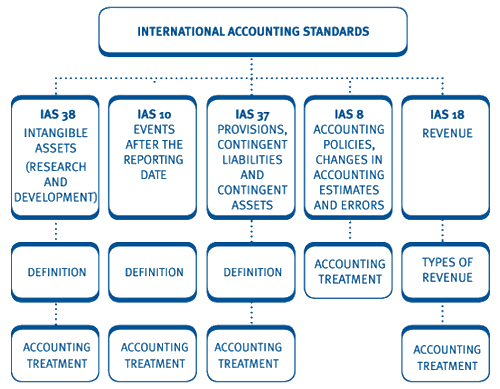
Revenue definition as per accounting standard. As per ias 18 a transaction is not regarded as generating revenue if goods or services are exchanged for goods or services of a similar nature and value. Revenue is recognised when it is probable that future. The objective of this standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment of revenue arising from certain types of transactions and events. Fees interest dividends and royalties.
However one can refer to ias 18 which deals with revenue. The gross inflow of economic benefits cash receivables other assets arising from the ordinary operating activities of an entity such as sales of goods sales of services interest royalties and dividends. Accounting standard or as 9 defines revenue as revenue is the gross inflow of cash receivables or other consideration arising in the course of the ordinary activities of an enterprise from the sale of goods from the rendering of services and from the use by others of enterprise resources yielding interest. The primary issue in accounting for revenue is determining when to recognise revenue.
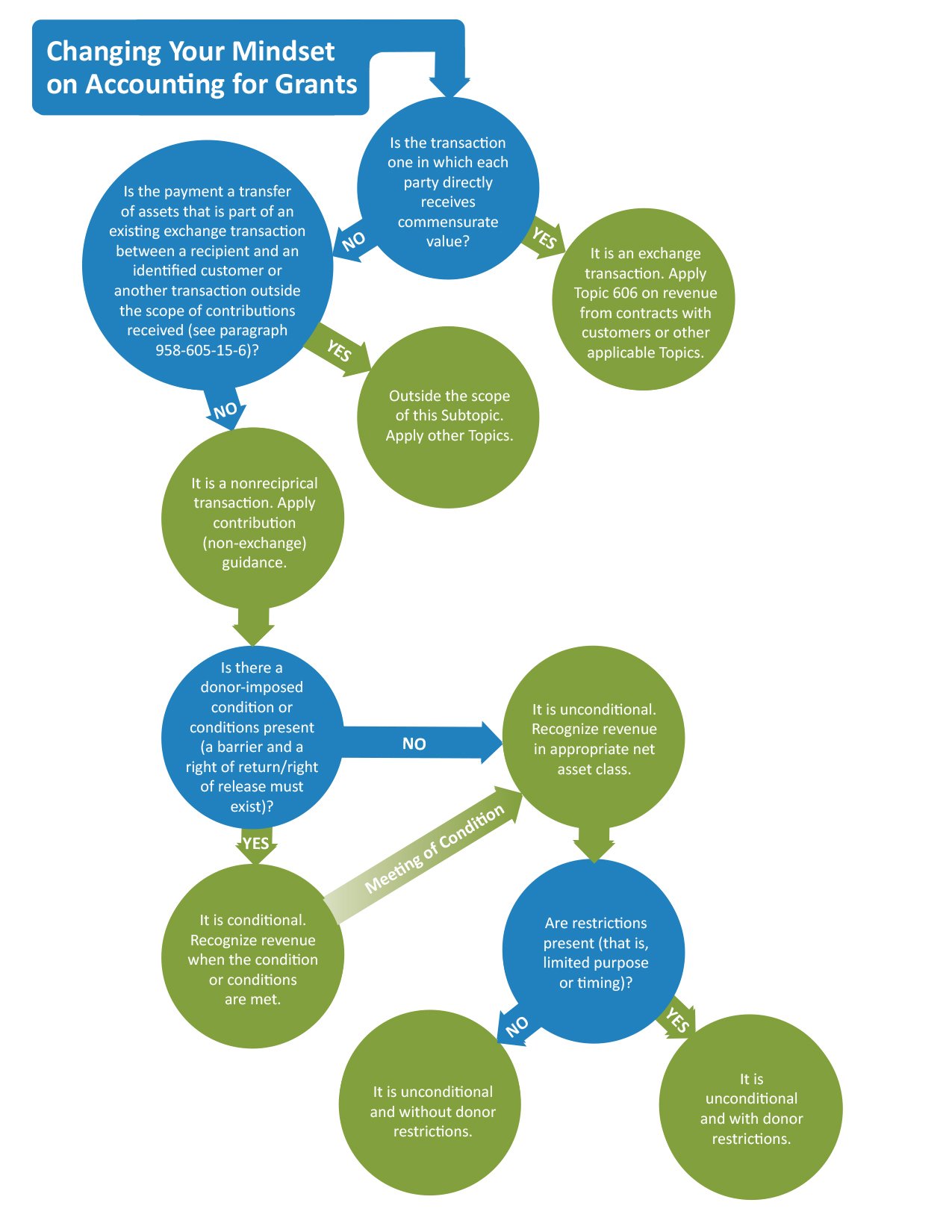
The new standard replaces existing ifrs revenue recognition guidance may result in a substantial change in the amount and timing of revenue recognition significantly more qualitative and quantitative disclosures are required. Under the accrual basis of accounting revenues are recorded at the time of delivering the service or the merchandise even if cash is not received at the time of delivery. Revenue recognition is a generally accepted accounting principle gaap that identifies the specific conditions in which revenue is recognized and determines how to account for it. An accounting standard is a common set of principles standards and procedures that define the basis of financial accounting policies and practices.
Accounting standards apply to the full breadth.