Revenue In Accounting Means

Accounting offsets are less necessary for capital expenditures relating to research and development because r d ultimately leads to new revenue streams.
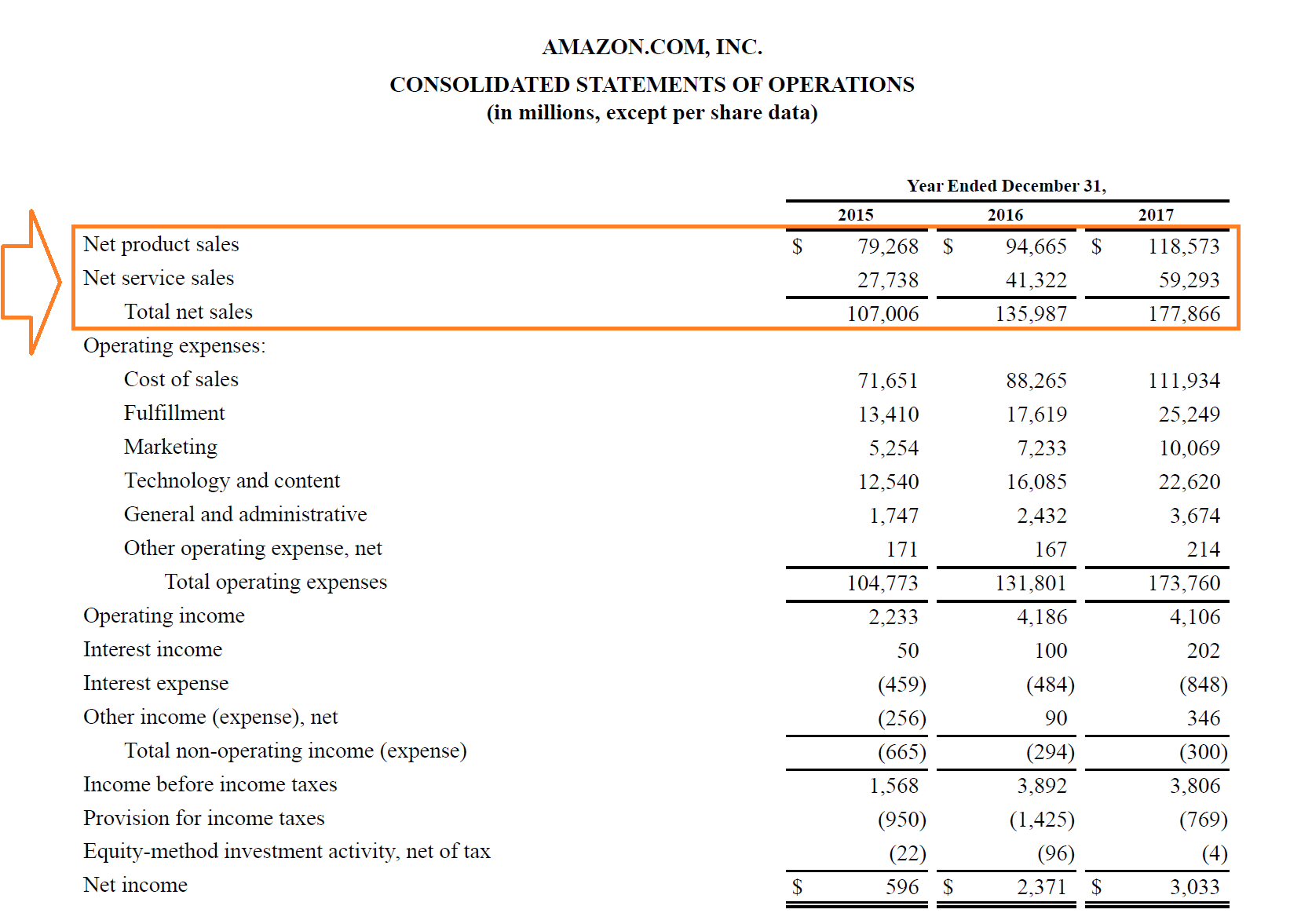
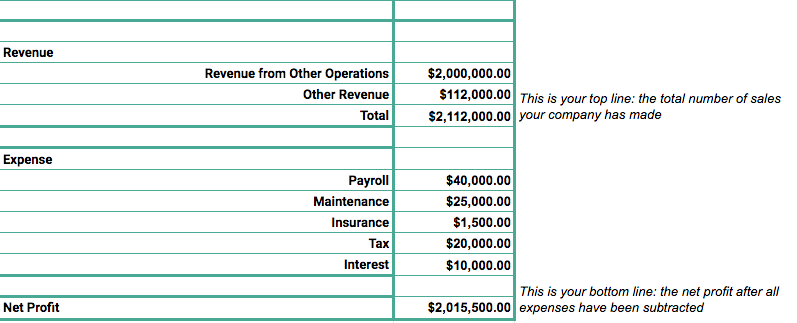
Revenue in accounting means. Revenue may refer to income in general or it may refer to. There were many standards governing revenue recognition which have been consolidated into the gaap standard relating to contracts with customers. The income that a government or. According to american accounting association revenue is the monetary expression of the aggregate of products or services transferred by an enterprise to its customers during a period of time.
This makes sense because the revenue account is supposed to record the income earned in the current period. Although companies looking to save a little bit on r d can partner with local universities to include graduate students working on a free internship basis or in exchange for a scholarship which would still be less costly than hiring full time. The income that a government or company receives regularly. Sales service revenues fees earned interest revenue interest income.
In other words revenues include the cash or receivables received by a company for the sale of its goods or services. But in a business concern revenue means sales proceeds of goods or services or it is the price of goods sold or services rendered to the customers. A survey produced quarterly by the census bureau that provides estimates of total operating revenue and percentage of revenue by customer class for communication key. For example if a new company sold 75 000 of goods in december but allows the customer to pay 30 days later the company s december sales are 75 000 even though no cash was received in december.
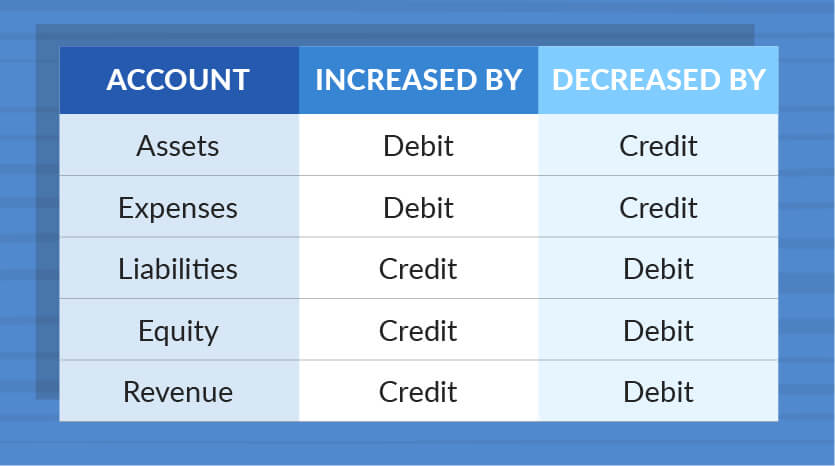
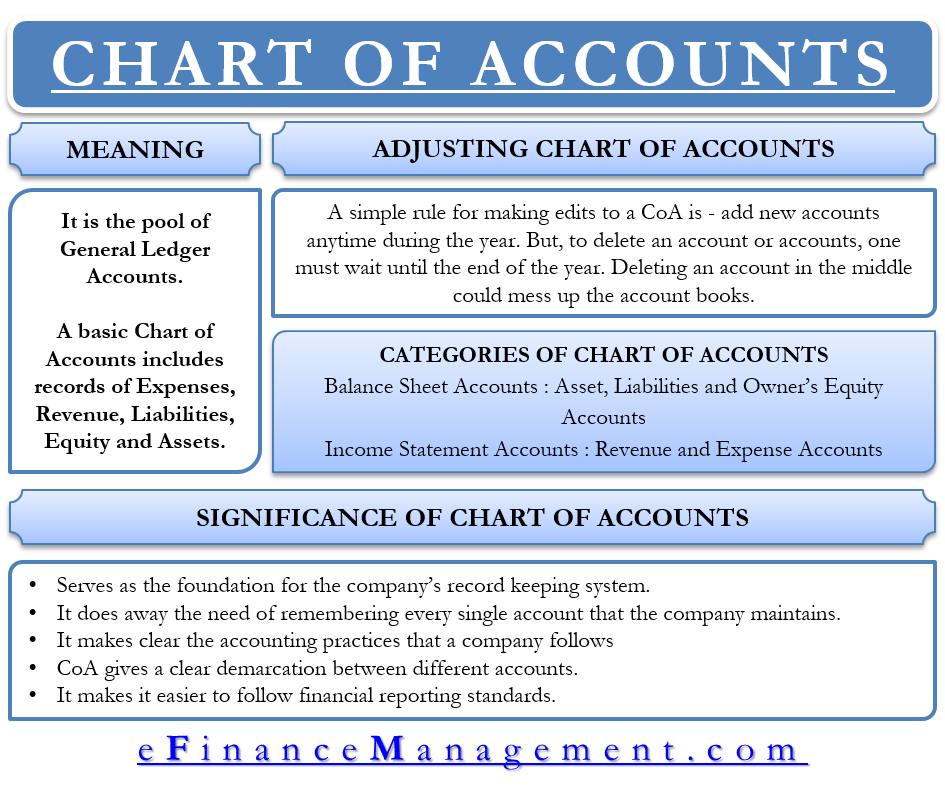
Often the term income is used instead of revenues. Under the accrual basis of accounting revenues are recorded at the time of delivering the service or the merchandise even if cash is not received at the time of delivery. Revenue account revenues are the assets earned by a company s operations and business activities. Types of revenues technically t.
In accounting revenue is the income or increase in net assets that an entity has from its normal activities in the case of a business usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. It s doesn t consist of a cumulative balance of all earnings in the company history. Thus revenue recognition is delayed under the cash basis of accounting when compared to the accrual basis of accounting. Examples of revenue accounts include.
.gif)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2020-10-27at3.34.43PM-253260b7e64f402aa5b3951a5d781292.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Apple10KIS-00e74dfe3f34479180ac7ede7b982292.jpg)






