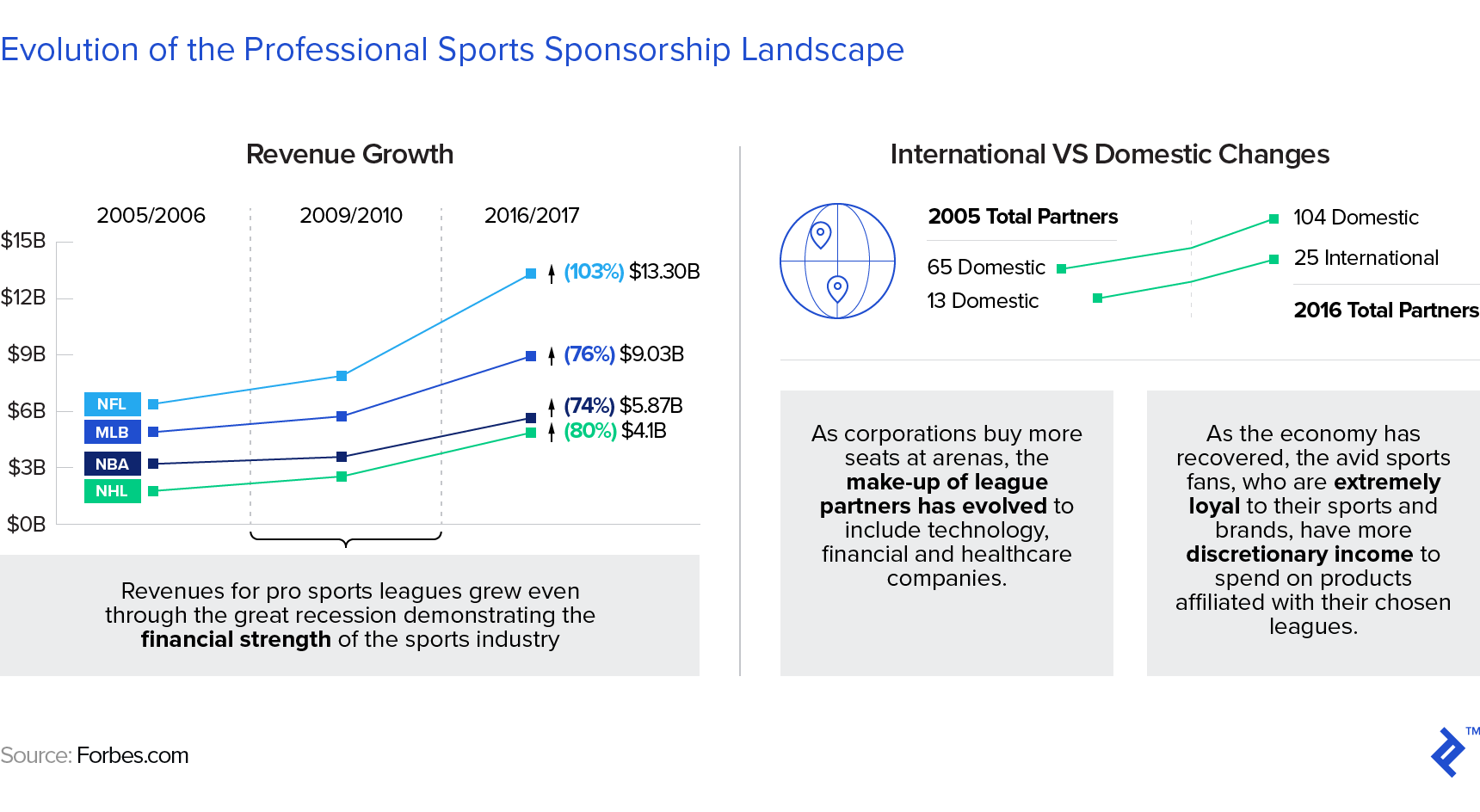
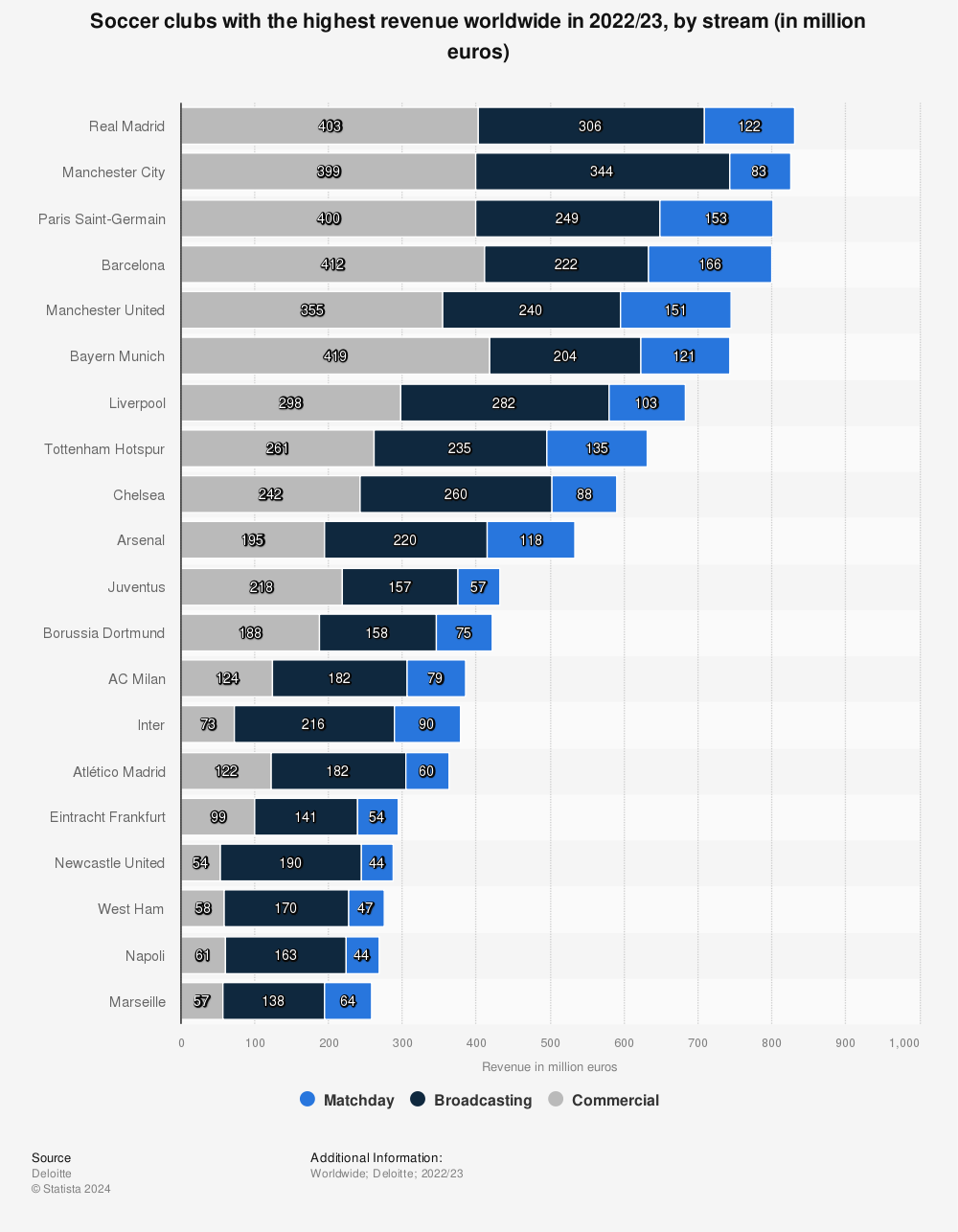
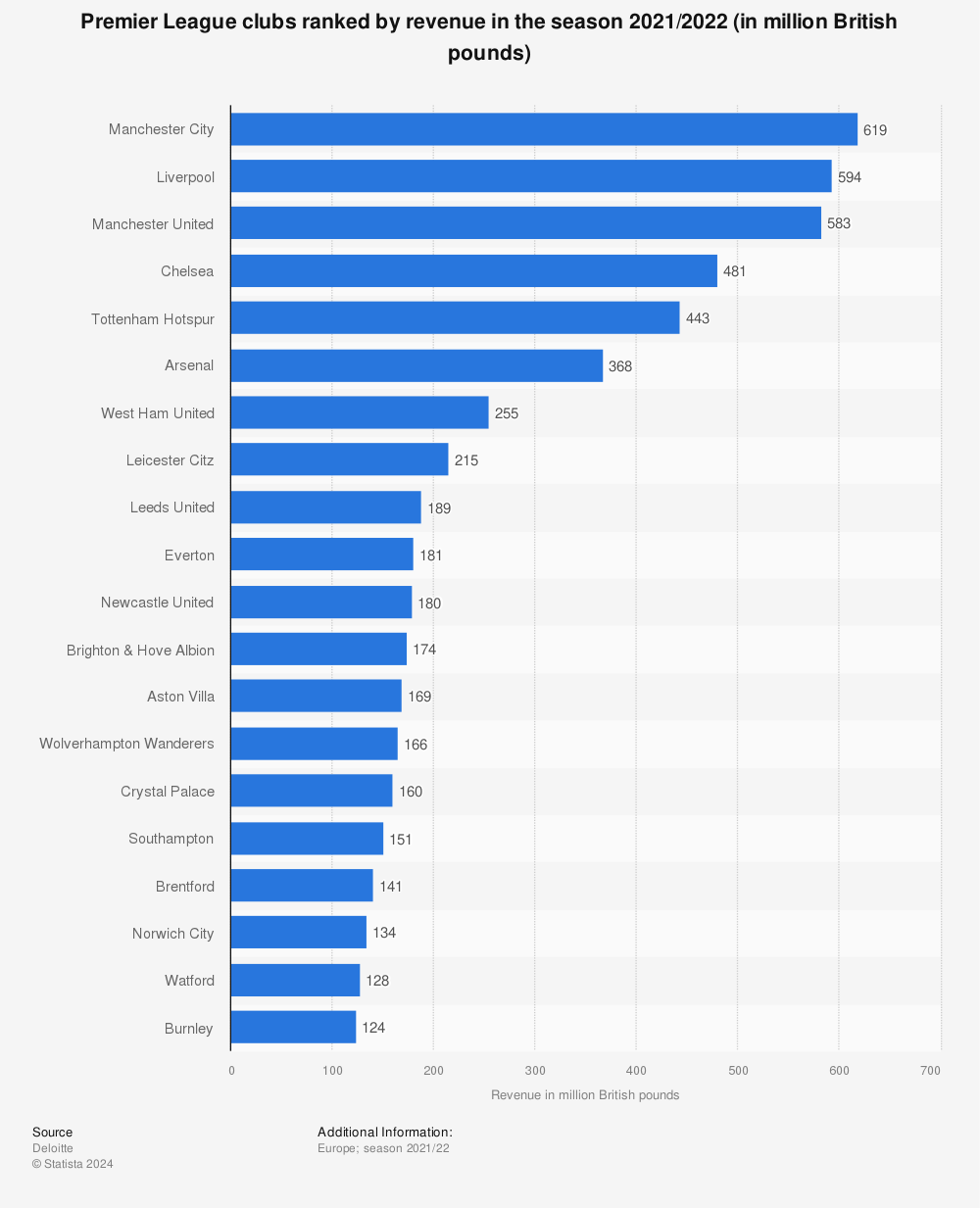
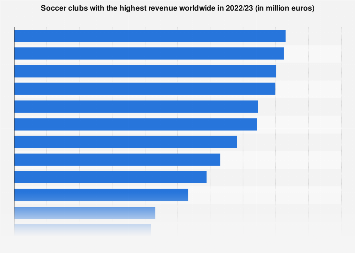
Revenue Sharing Professional Sports
Revenue sharing is used in sports as a way to improve competitive balance.
Revenue sharing professional sports. 2000 revenue sharing and competitive balance in professional team sports journal of sports economics 1. 1996 league management in professional team sports with win maximizing clubs european journal for sports management 2. We analyze the distribution of broadcasting revenues by sports leagues. Date of receipt of final manuscript.
The revenue effect reduces talent demand of each club because a part of the revenues is generated by competitors. Revenue sharing has been an important feature of models of professional sports leagues since fort and quirk 1995. Revenues of each club depend on absolute quality relative quality and on competitive balance itself so that our model captures much of the preceding literature as special cases. For the most part a large amount of research has focused on the effects of revenue sharing on league parity with little research on team profitability.
We show that revenue sharing always increases competitive. 24 october 2008 revenue sharing in professional sports leagues 265 r 2009 the authors journal compilation r 2009 scottish economic society. Revenue sharing structures in professional sports since the creation of profit sharing by the american football league in 1959 professional sports leagues have relied on revenue sharing to promote competitive balance among member organizations despite varying economic conditions and market capacities. To share or not to share.
The yearly revenue sharing has been an important feature of models of professional sports leagues since fort and quirk 1995. In the context of an isolated league we show that when the teams engage in competitive bidding to attract talent the league s optimal choice is full revenue sharing resulting in full competitive balance even if the revenues are independent of the level of balancedness. The impact of revenue sharing in a professional sports league. For the most part a large amount of research has focused on the effects of.
In professional sports leagues revenue sharing commonly refers to the distribution of proceeds generated by ticket sales to a given event. According to the sports economics literature if teams maximize their own respective profits then more talent will drift to the teams for which talent generates the. Individual revenues depend on both talent demand and competitive balance. It is felt that teams with larger revenue streams are able to afford more talent over the long run.
2004 the win maximization model reconsidered.