How To Calculate Differential Revenue

Revenue expenses income.
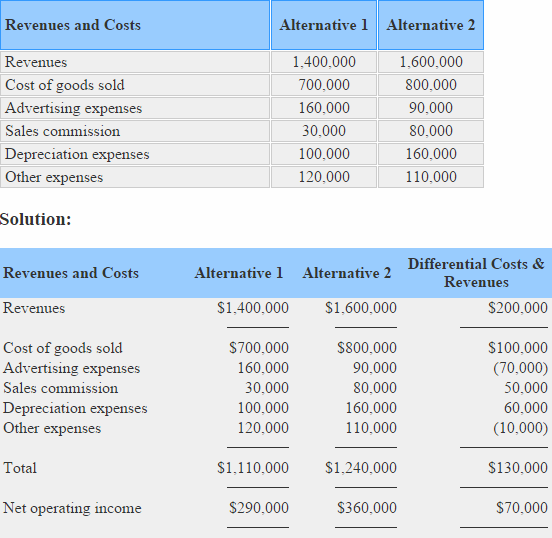
How to calculate differential revenue. Calculate the total revenues for each alternative and subtract the higher revenue alternative from the lower one to obtain differential revenue. Differential revenue defined when making business decisions it is typically the difference between the various alternatives that drives your decision making. The differential cost is compared to the differential revenue to determine the most profitable level of production and the best selling price. Differential analysis also called incremental analysis is a management accounting technique in which we examine only the changes in revenues costs and profits that result from a business decision instead of creating complete income statements for each alternative.
In essence you can line up the revenues and expenses from one decision next to similar information for the alternative decision and the difference between all line items in the two columns is the differential cost. For example a manager is pondering whether to invest in a new product line that will generate 1 000 000 of new sales or increase the marketing for an existing product line which will. The concept is commonly used when evaluating which of two or more investments to make in a business. Using differential revenue differential cost and differential income or loss calculations a company can decide between two or more alternative plans of action.
When a company needs to decide which product to launch first. When the differential revenue is higher than the differential cost the level of production is increased. The differential cost of the additional 5 000 widgets is 11 000. Differential income analysis then is when you compute differential income to make decisions.
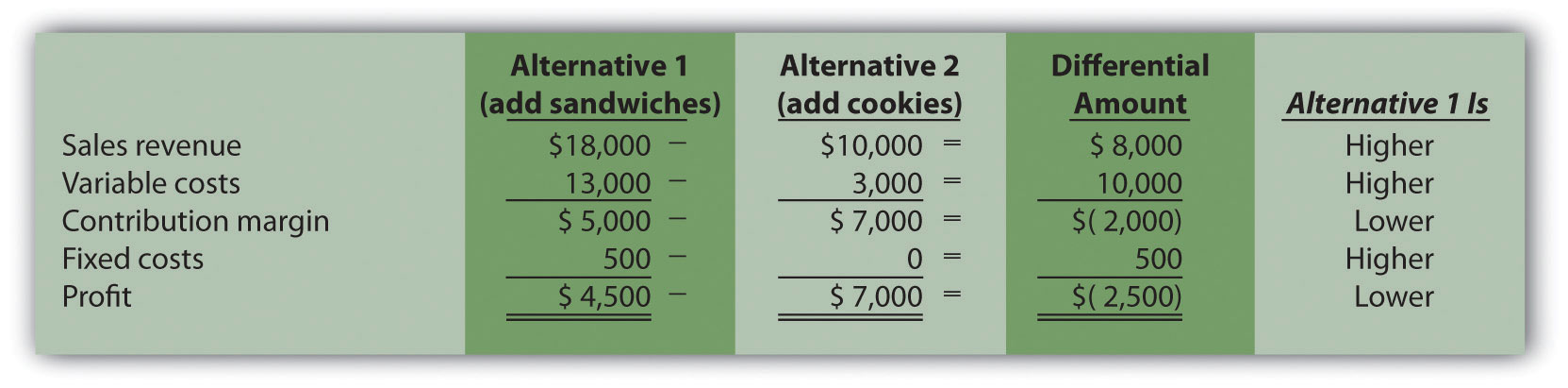
Offer a quotation at a lower selling price to increase capacity. Differential analysis involves analyzing the different costs and benefits that would arise from alternative solutions to a particular problem relevant revenues or costs in a given situation are future revenues or costs that differ depending on the alternative course of action selected differential revenue is the difference in revenues between two alternatives. In speaking of changes in cost and revenue the economists employ the term marginal cost and marginal revenue the revenue that can be obtained from selling one more unit of product is called marginal revenue and the cost involved in producing one more unit of a product is called marginal cost. Differential revenue and differential revenue analysis can be seen in many form including.
When a company invests in a new market. Even if you haven t seen the equation. Differential revenue is the difference in sales that will be generated by two different courses of action.




/dotdash_Final_Capital_Expenditures_vs_Revenue_Expenditures_Whats_the_Difference_2020-01-160a38c63f364966bfc46acc4b6b2917.jpg)











