Marginal Revenue Is Less Than Price

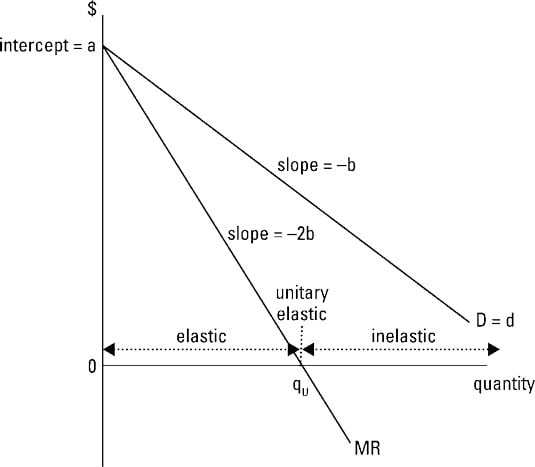
In a monopoly the marginal revenue is lower than the price because the demand curve is downward sloping.
Marginal revenue is less than price. The total revenue is calculated by multiplying the price by the quantity produced. Because a monopolist must lower its price in order to sell another unit of output marginal revenue is less than price. When a firm working under monopolistic competition sells more the price of its product falls. In every unit your changing revenue is going to be less than the week before and that is because you have to price the same price even to the same people you were selling to before a higher price.
Marginal revenue therefore must be less than price. In a monopoly the marginal revenue is always less than the price because there. And you can see that when you look at the column that says marginal revenue. When prices increase the quantity demanded declines while when the price declines the quantity demanded increases.
The implication of marginal revenue curve lying below average revenue curve is that the marginal revenue will be less than the price or average revenue. When prices go down more units of the product are bought. Marginal revenue is the rate of change in total rev enue as output sale changes by one unit. Therefore the sale price of a single additional item sold equals marginal revenue.
The total revenue from producing 21 units is 205. Because of this marginal. Could have sold these prior units at a higher price if it had not produced and sold the extra output. Could have sold these prior units at a price equal to marginal cost b.
So the firm is a price taker. In perfect competition marginal revenue is al ways equal to average revenue or price because the firm can sell as much as it like at the going market price. For example a company sells its first 100 items for a total of 1 000. Marginal revenue is less than price at every unit of output because the monopolist a.
Marginal revenue is less than the price of the product. In this case the total revenue is 200 or 10 x 20. In a monopoly the marginal revenue is lower than the price because the demand curve is downward sloping.