Marginal Revenue Product Economics Definition

This is also termed value of the marginal product.
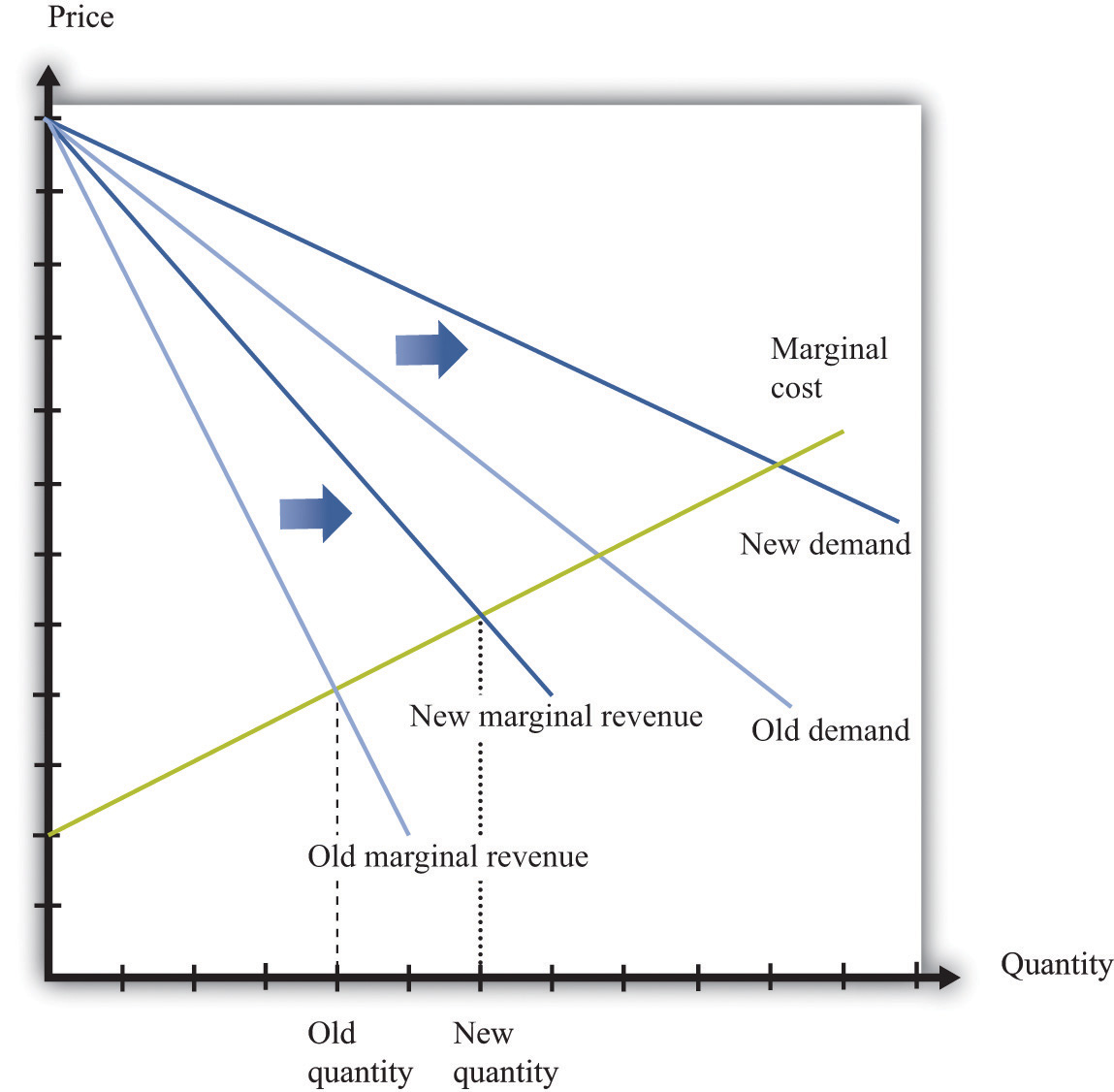
Marginal revenue product economics definition. Marginal revenue is the additional income generated from the sale of one more unit of a good or service. Marginal revenue product mrp. Marginal revenue product mrp also known as the marginal value product is the market value of one additional unit of output. Marginal revenue in perfectly competitive markets.
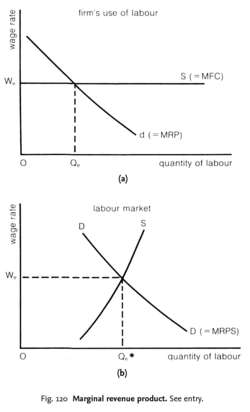
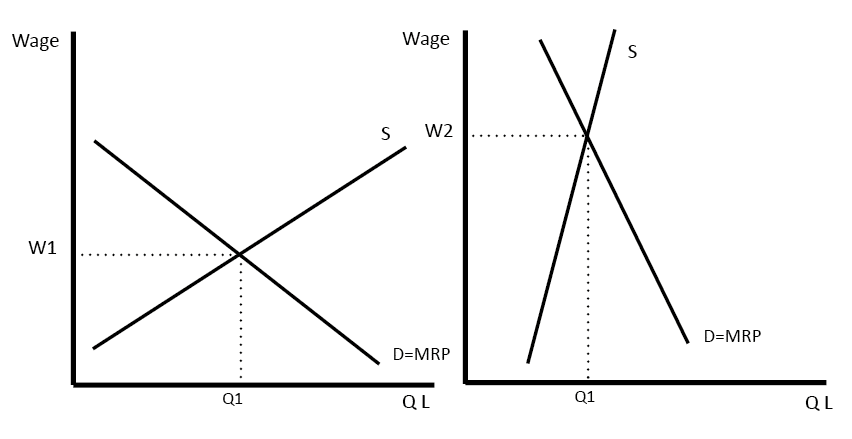
Marginal revenue is closely linked to marginal cost which measures the change in total cost from producing one extra unit of a product. Marginal revenue definition. The change in total revenue resulting from a unit change in a variable input keeping all other inputs unchanged marginal revenue product usually abbreviated mrp is found by dividing the change in total revenue by the change in the variable input. The demand curve for labour tells us how many workers a business will employ at a given wage rate in a given time period in the theory of competitive labour markets the demand curve for labour comes from the estimated marginal.
In a perfectly competitive market or one in which no firm is large enough to hold the market power to set price of a good if a business were to sell a mass produced good and sells all of its goods at market price then the marginal revenue would simply be equivalent to the market price. When marginal revenue is less than the marginal cost of a product a company is producing too much and should cut down its quantity until marginal revenue equals the margin cost of production so profits are. Marginal revenue mr is the incremental gain produced by selling an additional unit. But because the conditions required for perfect.
Term marginal revenue product definition. This article focuses on the term s meaning in economics. To analyze consumer demand or demand of the product in the market misjudging of customer demand leads to a shortage of products and loss of sales and production in excess leads to excess manufacturing cost. It is all about adding one more onto the pile and measuring the extra pleasure cost tax revenue price amount saved amount spent amount produced etc.
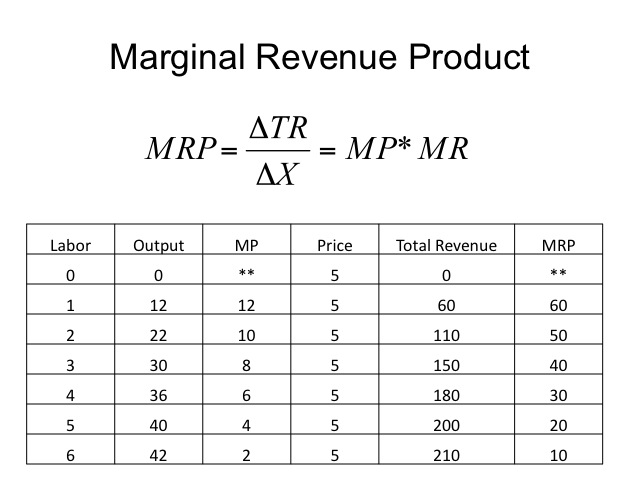
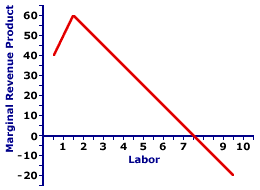
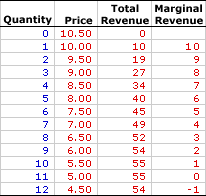
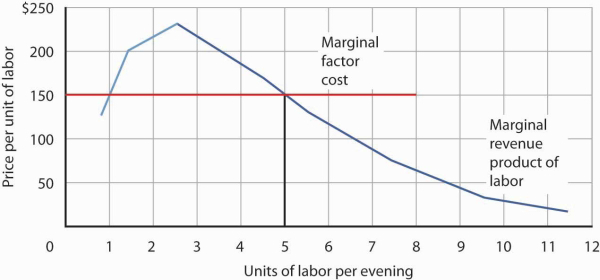
The marginal revenue product is. 11 units and the total revenue generated from selling one extra unit i e. It follows the law of diminishing returns eroding as output levels increase.