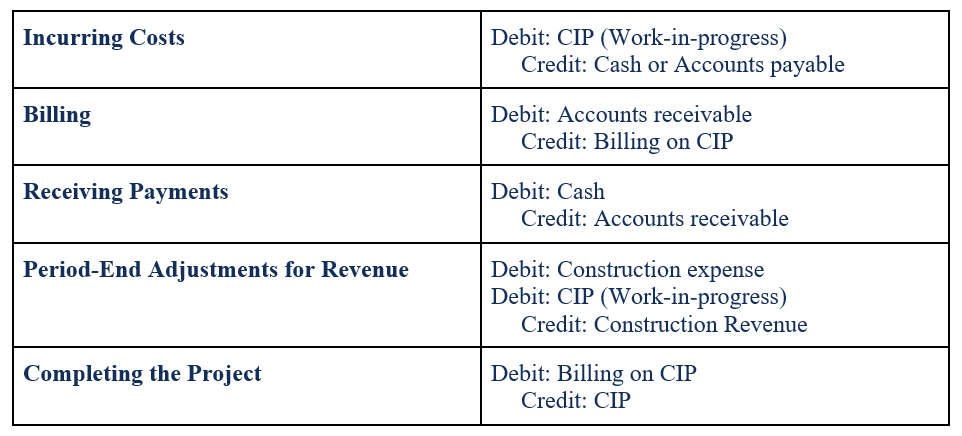
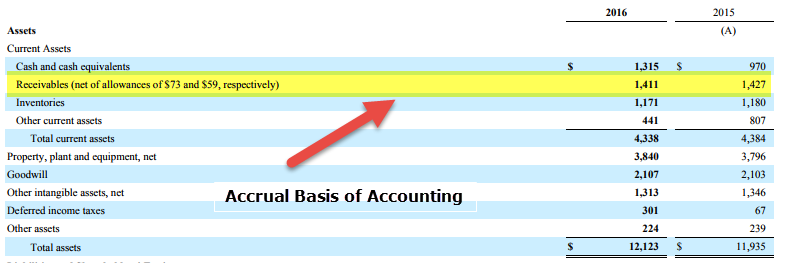
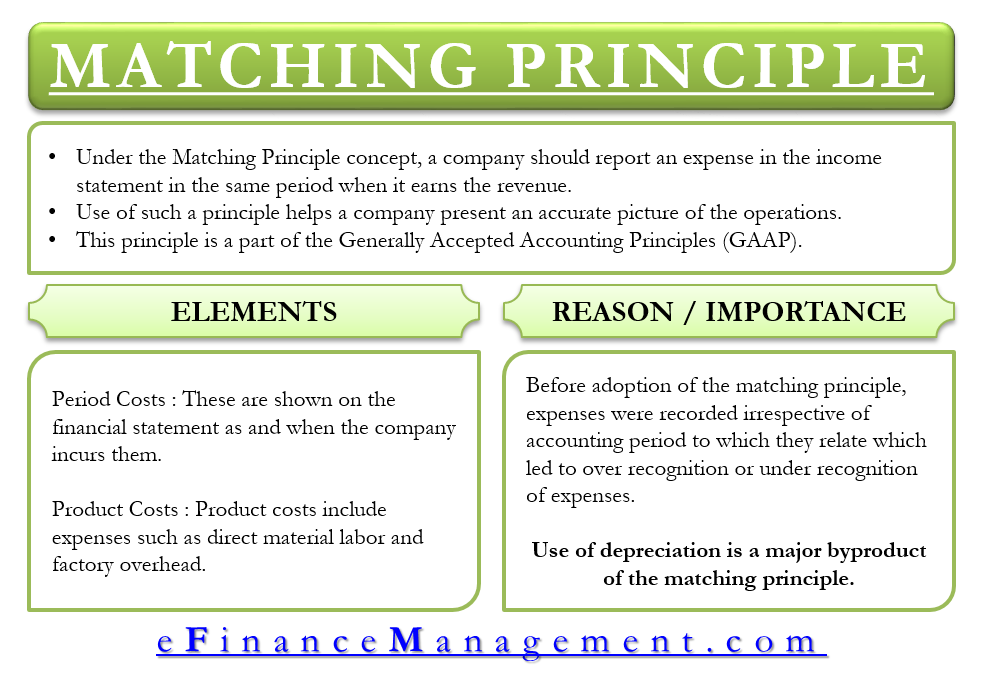
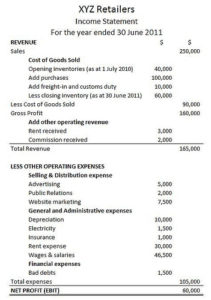
Revenue Recognition Principle Accounting Example

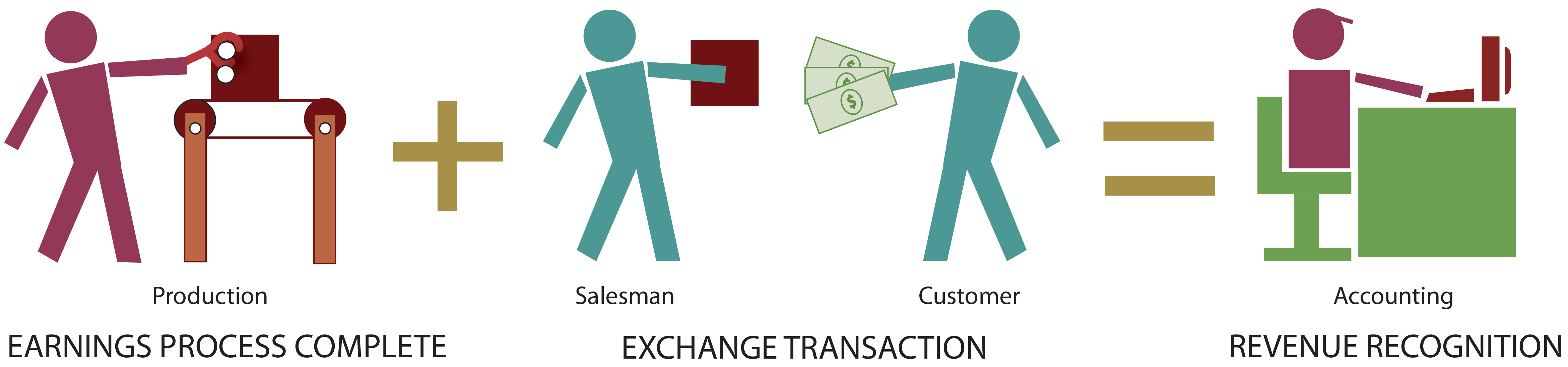
Revenue recognition is a generally accepted accounting principle gaap that stipulates how and when revenue is to be recognized.
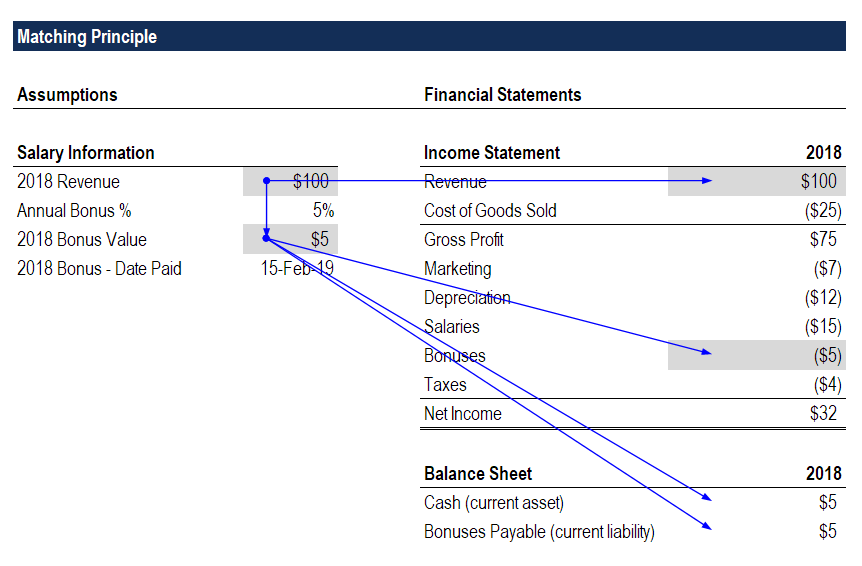
Revenue recognition principle accounting example. Here is the detail of revenue recognition principle. There are many principles that use to recognize revenue in the financial statements. The revenue recognition principle states that revenue should only be realized once the goods or services being purchased have been delivered. 13 time period principle.
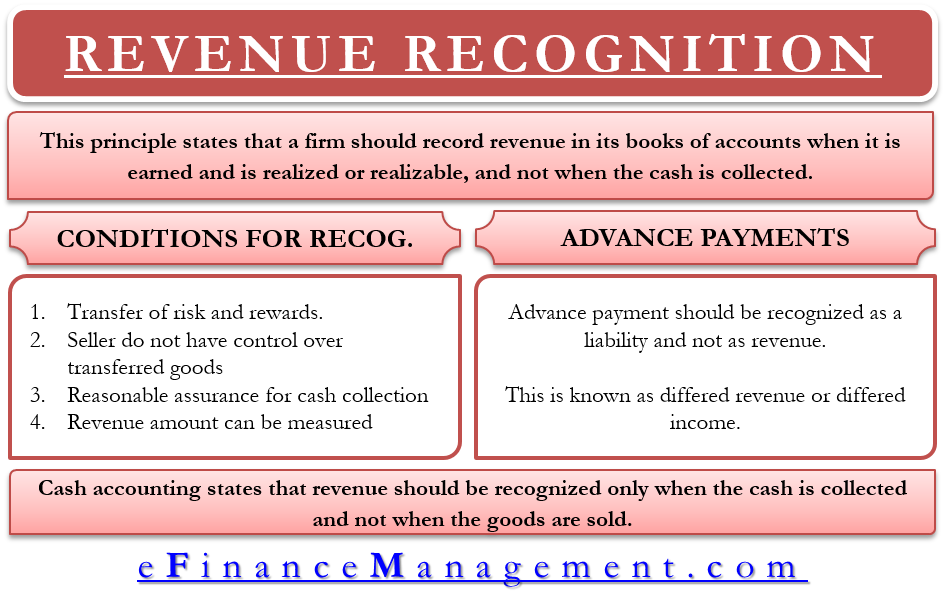
Cash accounting states that revenue should be recognized only when the cash is collected and not when the goods are sold. Revenue recognition principle a part of accrual accounting is superior to cash accounting. The revenue recognition could be different from one accounting principle to another principle and one standard to another standard. In accounting the terms sales and revenue can be and often are used interchangeably to mean the same thing.
Revenue recognition vs cash accounting. Recently accounting for revenue has undergone significant changes as a result of iasb and fasb attempting to converge revenue recognition under ifrs and us gaap. Revenue recognition principle requires that a company must recognize revenue only when the goods or services are transferred to the customer and not when the associated cash flows occur. For example based on a cash basis or cash accounting principle revenue is recognized in the financial statements at the time cash is received.
For example accrual basis or cash basis. This is a form of cash basis accounting and is most commonly found in installment sales. In accrual accounting principle revenue should be recognized when risks and rewards are transferred. The opposite of the revenue recognition principle is cash accounting.
The revenue recognition principle using accrual accounting. 12 revenue recognition principle. The last exception to the revenue recognition principle is companies that recognize revenue when the cash is actually received. Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that outlines the specific conditions under which revenue sales revenue sales revenue is the income received by a company from its sales of goods or the provision of services.
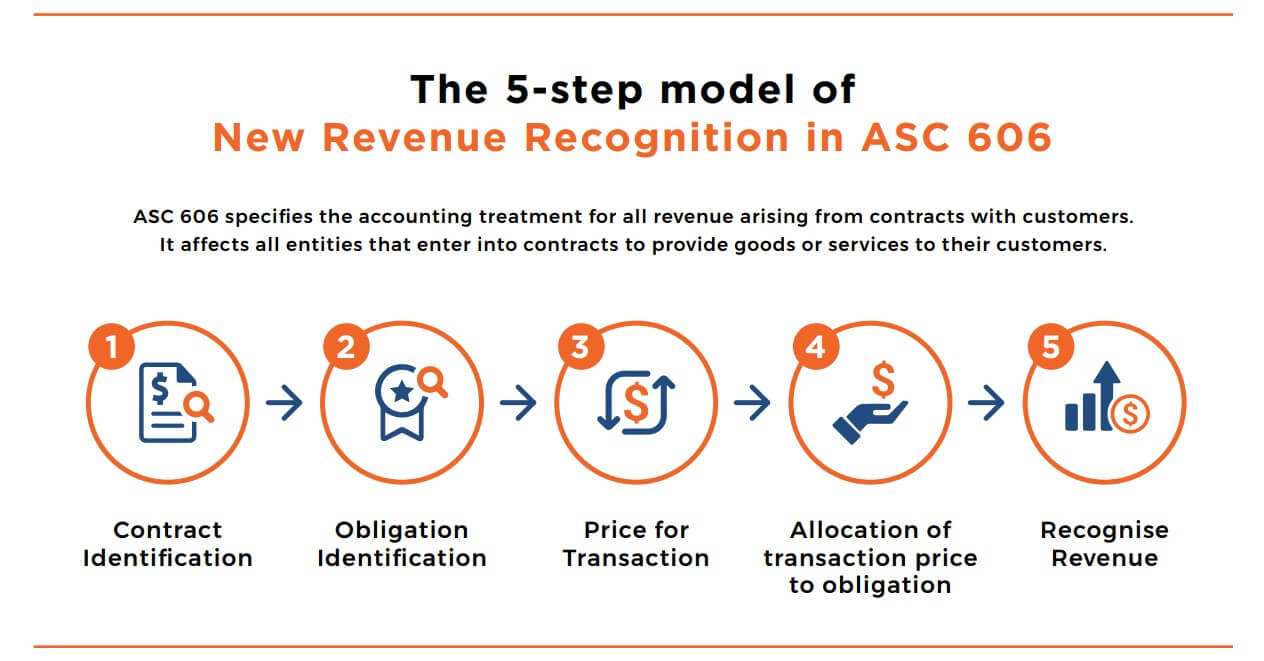
Requirements for revenue recognition.