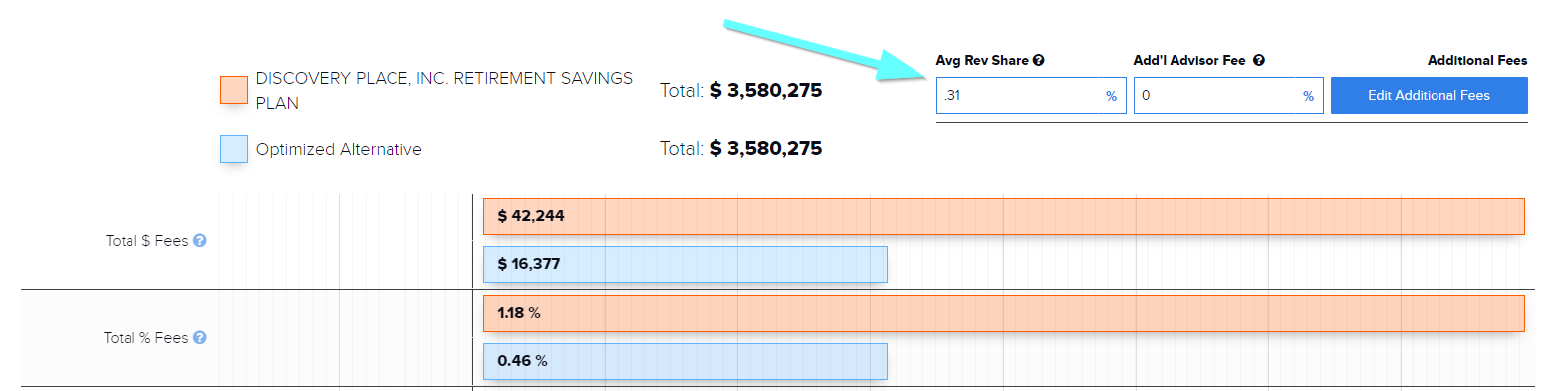
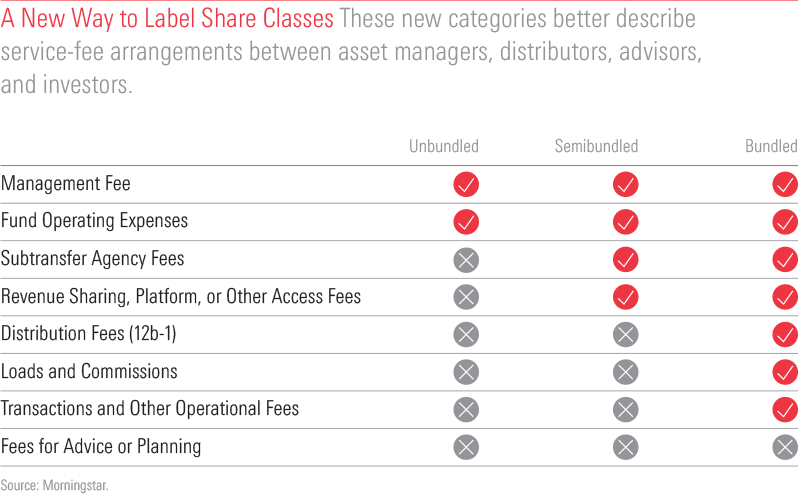
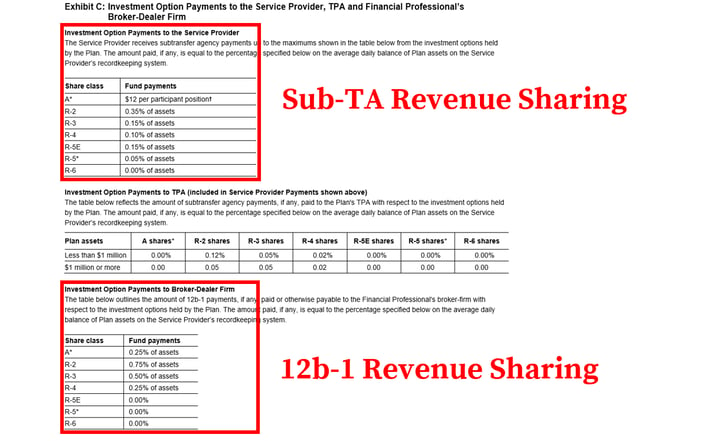
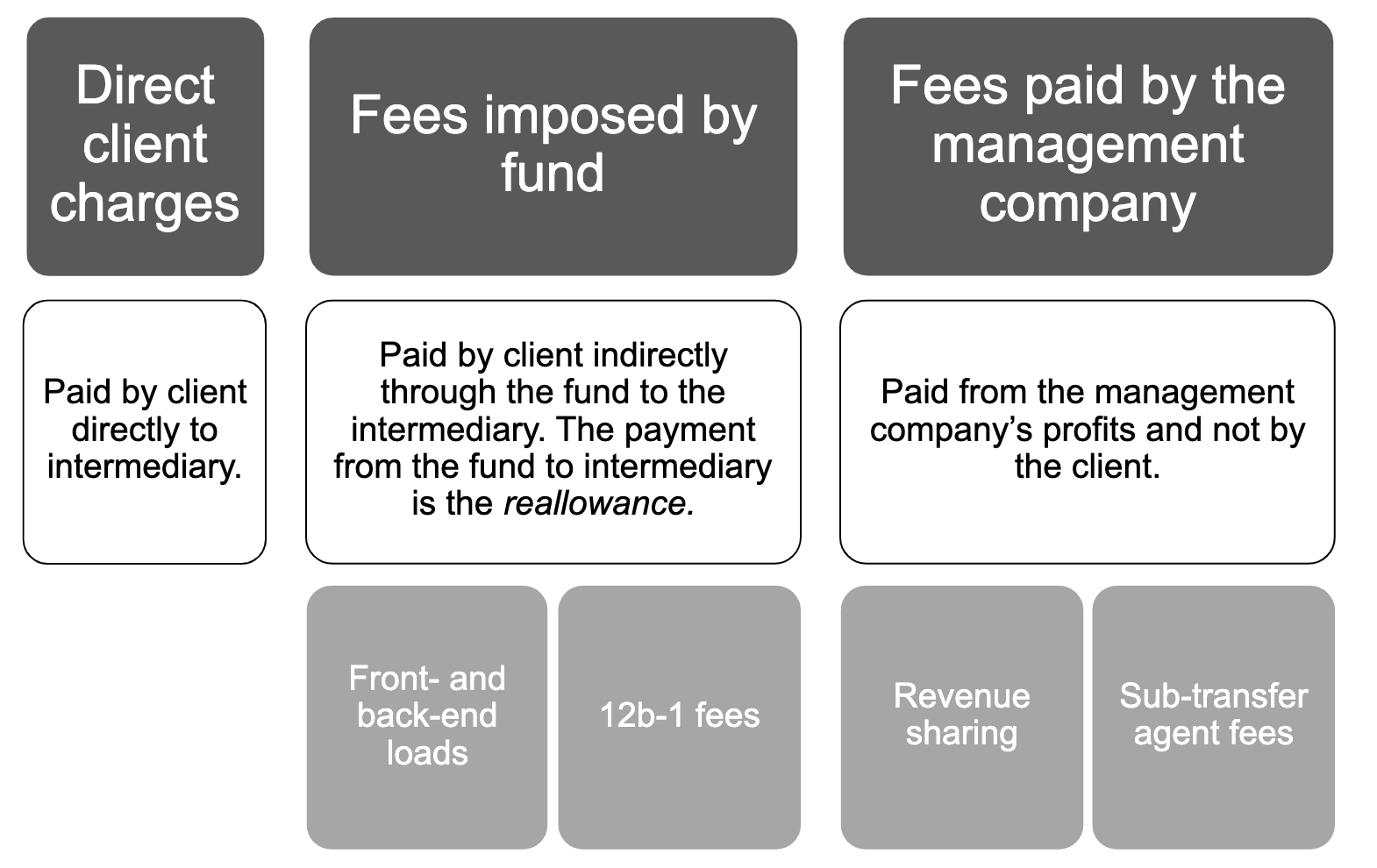
Revenue Sharing Vs 12b 1

The world of fund distribution to intermediaries for sales of fund shares is not quantum physics but it is much more hidden and convoluted than logic and law requires.
Revenue sharing vs 12b 1. That the broker dealer and ria engaged in conflicts associated with revenue sharing tied to 12b 1 fees. There are several regulatory nuanced and interpretive discussions of mutual fund distribution issues including revenue sharing 12b 1 fees and defensive 12b 1 plans. Distribution 12b 1 fees. The only difference between a retail fund and an institutional fund is the fees they charge but that difference is a big one and that s why the decision may result in collateral damage to such fees with particular attention on 12 b 1 fees that are set deliberately high in order to pay by revenue sharing all the vendors involved in.
The scf case involved the receipt of revenue sharing as well as 12b 1 fees an expansion of the areas the sec reviewed in the share class initiative. Share classes that don t charge 12b 1 fees but do charge for revenue sharing have reported inflows according to morningstar. 1 the faq specifically focused on compensation from 12b 1 fees and revenue sharing arrangements in connection with mutual fund share class selection practices along with compensation in the form of the. The first form of revenue sharing 12b 1 fees is used for the cost of the sale or distribution of investments.
The fee is ordinarily paid to a broker dealer as a part of the distribution of the mutual fund. Which of these 12b 1 fees are charged depends on the share class. In a november speech sec enforcement director. 12b 1 fees collected from the fund.
Class a fund shares which often carry a front end load and no load mutual funds normally only charge a service fee but class b and c shares which charge a back end load will usually have higher 12b 1 fees. The fee is deducted from the assets of the mutual funds and thus is charged directly to the participants invested in that fund. A 12b 1 fee is an annual marketing or distribution fee on a mutual fund. Revenue sharing typically comes in two different forms.
They gained 183 billion in assets in 2018 and 581 billion the. Paid by mutual funds to cover costs related to marketing and distributing fund shares such as compensating advisors for selling fund shares and covering the costs of advertising and delivery of prospectuses to shareholders.